⇒ sin (sin − 1 x) = sin (2 π − sin − 1 y), take sine both sides ⇒ x = cos ( sin − 1 y ) , since sin ( 9 0 o − θ ) = cos θ ⇒ x = cos ( cos − 1 1 − y 2 ) = 1 − y 2$$sin^2(θ) cos^2(θ) = 1$$ $$tan^2(θ) 1 = sec^2(θ)$$ $$1 cot^2(θ) = csc^2(θ)$$ Cofunction Identities Each of the trig functions equals its cofunction evaluated at the complementary angle $$sin(θ) = cos({π/2} θ)$$ $$cos(θ) = sin({π/2} θ)$$ $$tan(θ) = cot({π/2} θ)$$ $$cot(θ) = tan({π/2} θ)$$ $$csc(θ) = sec({π/2} θ)$$The second shows how we can express cos θ in terms of sin θ Note sin 2 θ "sine squared theta" means (sin θ) 2 Problem 3 A 345 triangle is rightangled a) Why?
Trigonometric Functions
Sin 3 pi by 2 minus theta is equal to
Sin 3 pi by 2 minus theta is equal to-∴ sin(π/2 θ/3) = √3/2 ⇒ cos(θ/3) = cos 30 ° If an angle is α is divided into two parts A and B such that A B = x and tan A tan B = 2 1, then what is sinx equal to ?The exact value of arcsin( √2 2) arcsin ( 2 2) is π 4 π 4 x = π 4 x = π 4 The sine function is positive in the first and second quadrants To find the second solution, subtract the reference angle from π π to find the solution in the second quadrant x = π− π 4 x = π π 4 Simplify π − π 4 π π



The Trigonometric Ratios Of Angl
The equations in matrix form are R = x ¯ y ¯ = cos θ − sin θ sin θ cos θ x y Example 16 Rotate the line y = 5 x 1 an angle of 30° counterclockwise Graph the original and the rotated line Since 30° is π/ 6 radians, the rotation matrix is cos π 6 − sin π 6 sin π 6 cos π 6 = 0866 − 05 05 0866 Now compute the rotationAnswer (2) 1 Solution sin (π θ) sin (π – θ) cosec 2 θ = (sin θ) (sin θ) cosec 2 θ = sin 2 θ cosec 2 θ = sin 2 θ (1/sin 2 θ) = 1Examples of quadrantal angles include, 0, π/2 , π , and 3π/ 2 Angles coterminal with these angles are, of course, also quadrantal We are interested in finding the six trigonometric functional values of these special angles, and we will begin with θ = 0 Since any point (x, y) on the terminal ray of an angle with measure 0 has y coordinate equal to 0, we know that r = x, and we have,
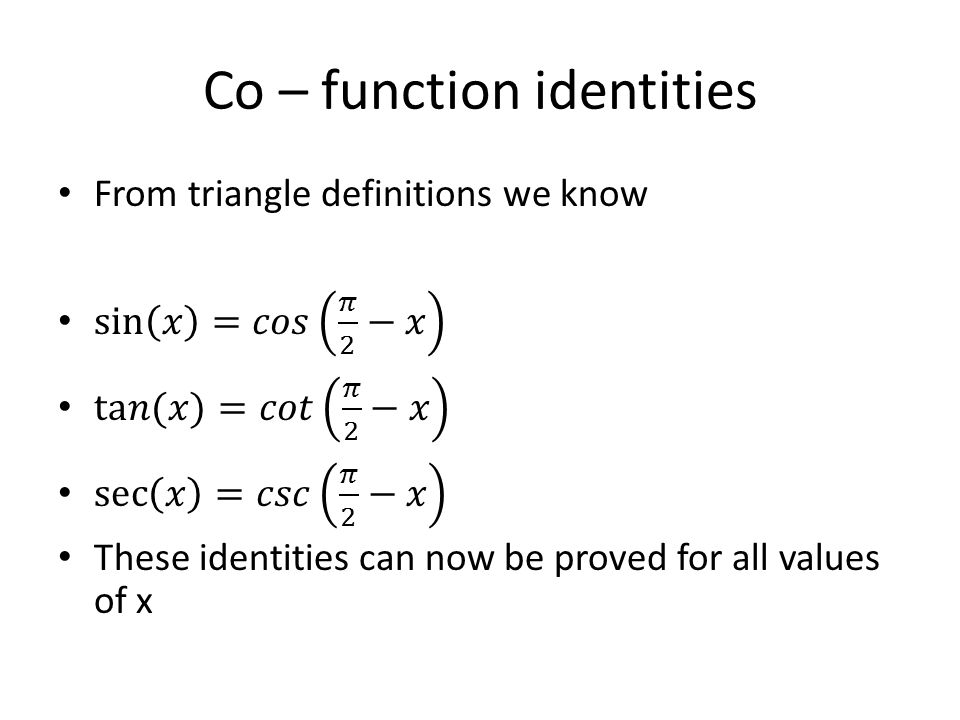
KEAM 17 tan((π/4) (θ/2)) tan((π/4) (θ/2)) is equal to (A) sec θ (B) 2 sec θ sec (θ /2) (D) sin θ (E) cos θMore Trigonometry Questions Q1 There are two vessels in the sea, opposite side of a lighthouse The angle of elevation of the top of the lighthouse isThe complementary angle equals the given angle subtracted from a right angle, 90° For instance, if the angle is 30°, then its complement is 60° Generally, for any angle θ, cos θ = sin (90° – θ) Written in terms of radian measurement, this identity becomes cos θ = sin (π/2 – θ
Rewrite the middle terms as a perfect square ρ = sin θ sin φ ρ 2 = ρ sin θ sin φ Multiply both sides of the equation by ρ x 2 y 2 z 2 = y Substitute rectangular variables using the equations above x 2 y 2 − y z 2 = 0 Subtract y from both sides of the equation x 2 y 2 − y 1 4 z 2 = 1 4 Complete the square x 2 (ySolution sin 2 θ = 3 4 ⇒ sin θ = ± √ 3 2 ⇒ sin θ = sin (± π 3) ⇒ θ = nπ (1) n ∙ (± π 3 ), where, n ∈ Z ⇒ θ = nπ ± π 3, where, n ∈ Z Therefore the general solution of sin 2 θ = 3 4 is θ = nπ ± π 3, where, n ∈ Z Trigonometric Equations General solution of the equation sin x = ½And if 3π/2 < θ < 2π, cos(θ) is positive while sin(θ) and tan(θ) are negative As θ increases beyond 2π (or when θ decreases below 0) the same pattern is repeated
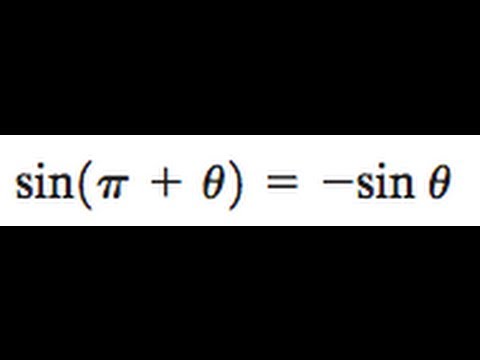



Sin Pi Theta Sin Theta Youtube
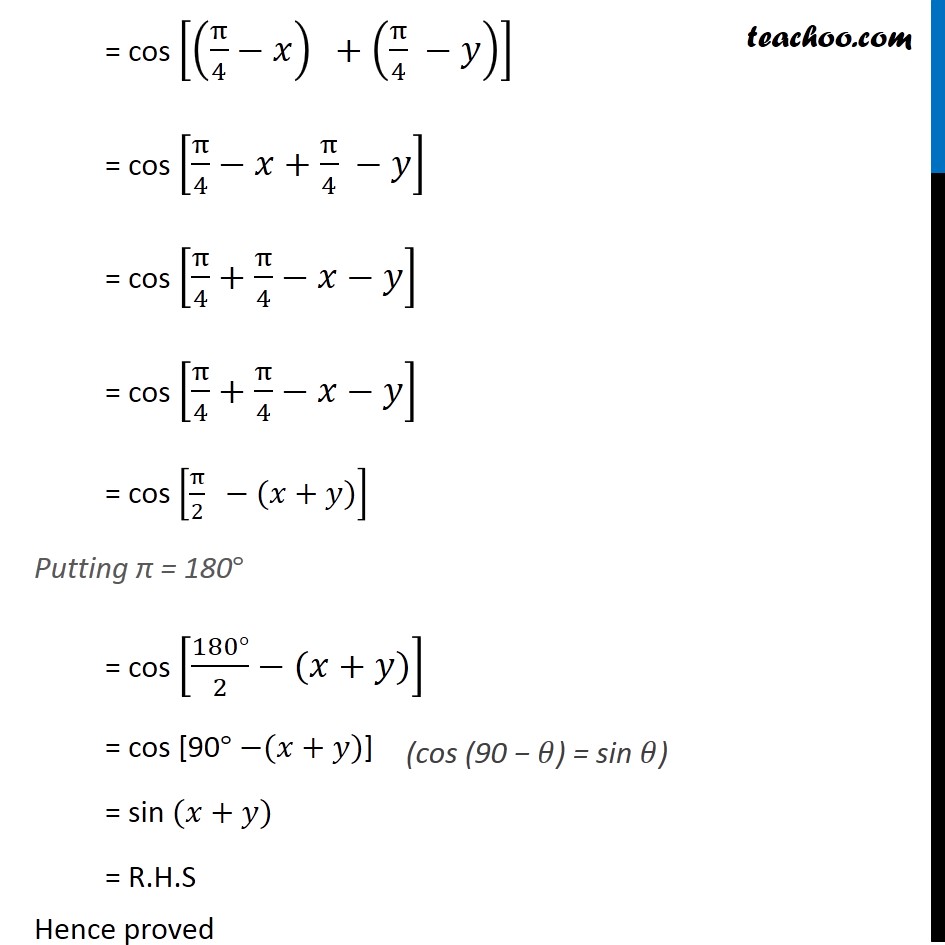



Ex 3 3 6 Prove That Cos Pi 4 X Cos Pi 4 Y Chapter 3
Therefore, we will leave the Solution Set Simple Harmonic Motion Physics 107 Answers Simple Harmonic Motion 1 The maximum displacement from the equilibrium position A = 100 cm The time for one complete oscillation T = π/2 s Notice the maximum positive displacement x = 100 cm occurs at t = 0 and the next time at t = π/2 sConverting these back to real part/imaginary part notation eiπ/4 = cos π 4 isin π 4 = 1 √ 2 i √ 2 and e5iπ/4 = cos 5π 4 isin 5π 4 = − 1 √ 2 − i √ 2 This exercise is part of an interesting subject in mathematics called the nth




Cosec P 2 Theta Xcos Theta Cot Theta P 2 Theta Sin P 2 Theta Find Value Of X Brainly In




If Tan Theta 3 4 And Theta Is Not In First Quadrant Then Sin Pi 2 Theta Cot Pi Theta Tan 3pi 2 Theta Cos 3pi 2 Theta
Find the slope of the normal to the curve x = 1 − a sin θ, y = b cos^2θ at θ=π/2 asked in Mathematics by sforrest072 (128k points) application of derivative;Sin (theta) = oppo/hypo we know that oppo = 2 by pythagoras theorem hypo = sqrt (oppo^2adj^2) therefore,hypo = sqrt (49) = therefore sin (theta) = 2/ = 055 but if theta is in third quadrant tan (theta) is positive while sin (theta) is negative therefore the answer is A) or 055Setting each of r, θ and z equal to a constant defines a surface in space, as illustrated in the following example To convert this spherical point to cylindrical, we have r = 6 sin (π / 2) = 6, θ
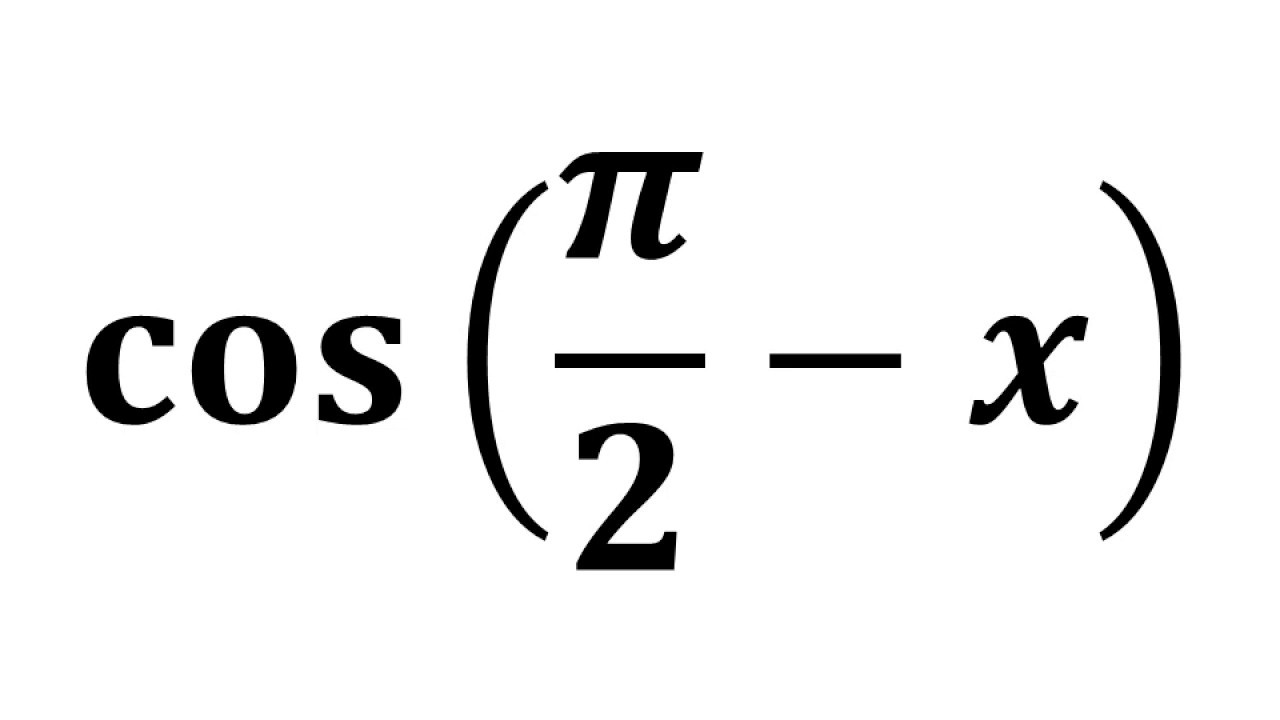



Cos Pi 2 X Cos Pi 2 Theta Youtube



Sine Function Sin X
If two angles add up to 90° or π/2, the sine of one is equal to the cosine of the other Also, the tangent of one is equal to the cotangent of the other θ and (π/2θ) are complimentary angles because θ (π/2θ) = π/2 By referring to the right triangle shownIt is given that sin (π/2 θ/3) = √3/2 Formula Used Basic concept of trigonometric ratio and identities We know that sin(90 θ) = cos θ ⇒ cos 30° = √3/2 Calculation We know that sin (π /2 θ) = cos θ ∴ sin(π/2 θ/3) = √3/2 ⇒ cos(θ/3) = cos 30° ⇒ θ/3 = 30° = θ = 90° Now, value of tan θ = tan 90° = Not defineTo see the answer, pass your mouse over the colored area To cover the answer again, click "Refresh" ("Reload")
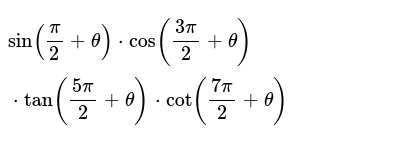



Sin Pi 2 Theta Cos 3pi 2 Theta Tan 5pi 2 Theta Cot 7pi 2 Theta




Content Graphing The Trigonometric Functions
Then the side opposite the angle x will have length sinx and the side opposite the angle ( π 2 −x) will have length sin( π 2 − x) By Pythagoras theorem, the sum of the squares of the lengths of these sides is equal to the square of the length of the hypotenuse So sin2x sin2( π 2 − x) = 12 = 1 Answer link 2340 sin θ − 1251 cos θ =2660 cos (θ 1081) Checking using a graph, we obtain the following for each side of our answer We see that our negative cosine curve has an amplitude of 2660 and it has been shifted to the left by 1081 radians, which is consistent with the expression −2660 cos ( θ 1081)COMEDK 05 If sin(π cos θ) = cos(π sin θ), then sin 2 θ equals (A) ± (3/4) (B) ± √2 ± (1/√3) (D) ± (1/2) Check Answer and Sol



3



Sin Theta Equals 0 General Solution Of The Equation Sin 8 0 Sin 8 0
Dius So the circles intersect also at θ = π/4, as the figure shows The area of the shaded region can thus be computed as the difference I1− I2 = 1 2 Z π π/4 sin2θdθ − 1 2 Z π/2 π/4 cos2θdθ of the area of the respective shaded regions in Now I1 = 1 4 Z π π/4 (1−cos2θ)dθ = 1 4 h θ − 1 2 sin2θ iπ π/4 = 1 4 3π 4 1 2Cos^2 ( pi6 theta ) sin^2 ( pi6 theta ) is equal toAsk a Question If sin θ = √3 cos θ, – π < θ < 0, then θ is equal to ← Prev Question Next Question →
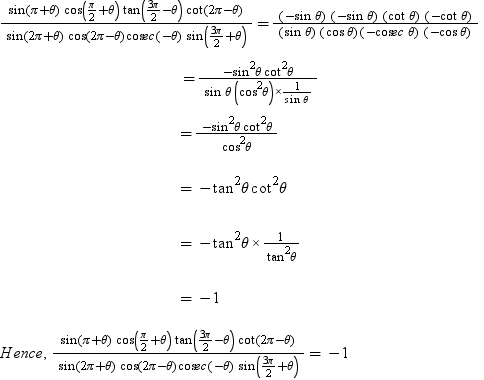



Evaluate Sin Pi Theta Cos Pi 2 Theta Tan 3pi 2 Theta Cot 2pi Theta Sin 2pi Theta Cos 2pi Theta Cosec Theta Sin 3pi 2 Theta Maths Trigonometric Functions Meritnation Com



How Do You Evaluate Sin Pi 6 Socratic
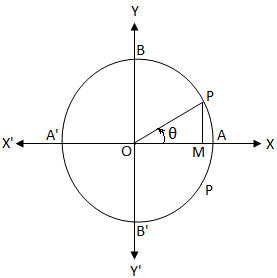
If we started from A and moves in anticlockwise direction then at the points A, B, A', B' and A, the arc length travelled are 0, π 2, π, 3 π 2, and 2π Therefore, from the above unit circle it is clear that sin θ = P M O P Now, sin θ = 0 ⇒ P M O P = 0Solution for Assume sin(θ)=18/29 where π/2Answer As we need to find the most general solution for two different trigonometric equations Tan θ = 1 (1) and cos θ = 1/√2 (2) Most general value of θ is the common solution of both equation 1 and 2 Let S 1 represents the solution set of equation 1 and S 2 be the solution set equation 2




Sin Pi 2 Theta Sin 3pi 2 Theta Sin 5pi 2 Theta Sin 7pi 2 Theta Is Equal To
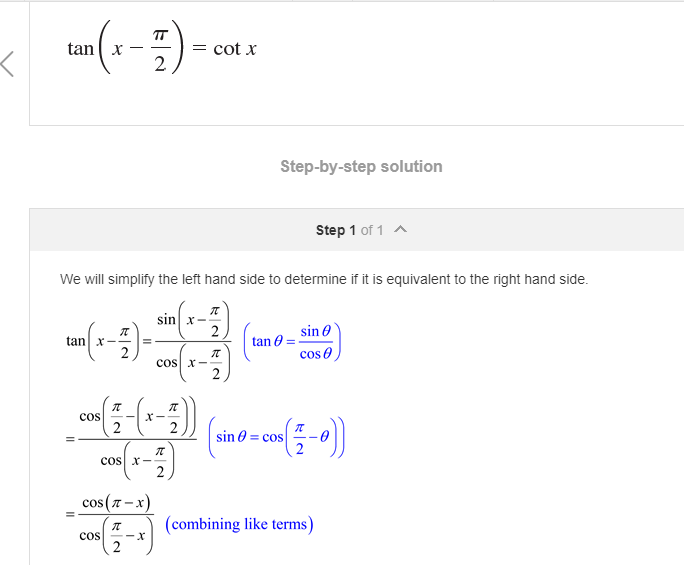



Can Someone Explain How Sin X Pi 2 Becomes The Chegg Com
Time between θ and θ dθ is equal to the number incident particles per unit time between b and b db Therefore, for incident flux j I, the number of particles scattered into the solid angle NdΩ=2 π sin θ dθ N =2πbdbj I0 votes 1 answer If tan ( π/4 θ) tan (π /4 − θ) = p sec 2θ, then find the value of p asked in Trigonometry by Gaangi (248k points)If tan(θ)= 15 / 8 , 0 ≤ θ ≤ (π / 2) , then sin(θ) equals cos(θ) equals sec(θ) equals Expert Answer Who are the experts?




In Cofunction Identity Sin 3 P 2 8 Is Equ Gauthmath
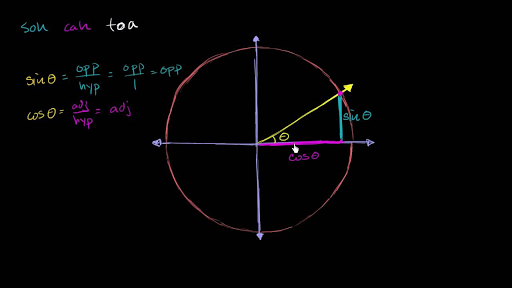



Sine Cosine Identities Periodicity Video Khan Academy
Similarly, when π < θ < 3π/2, x and y are both negative so sin(θ) and cos(θ) are negative while tan(θ) is positive;Proportionality constants are written within the image sin θ, cos θ, tan θ, where θ is the common measure of five acute angles In mathematics, the trigonometric functions (also called circular functions, angle functions or goniometric functions) are real functions which relate an angle of a rightangled triangle to ratios of two side lengths= lim θ→0 tan (π sin 2 θ) / sin (2π sin 2 θ) = lim θ→0 (1 / 2) {tan (π sin 2 θ) / π sin 2 θ} * {2π sin 2 θ / sin (2π sin 2 θ)} = – 1 / 2 Therefore, the correct answer is (a)




If Sin Pi Cottheta Cos Pitantheta Prove That Either Cosec 2theta Or Cot 2theta Is Equal To N Dfrac 1 4 Where N Is A Positive



What Is The Value Of Sin 3 Pi 2 Quora
The first shows how we can express sin θ in terms of cos θ;Sin (θ), Tan (θ), and 1 are the heights to the line starting from the x axis, while Cos (θ), 1, and Cot (θ) are lengths along the x axis starting from the origin The functions sine, cosine and tangent of an angle are sometimes referred to as the primary or basic trigonometric functionsExperts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high 100% (7 ratings)



Biomath Trigonometric Functions




Consider The Angle Theta In Standard Position In A Unit Circle Where 0 Is Less Than Or Equal To Theta Is Less Than Pi 2 Or Pi 2 Is Less Than Theta Is Less
Where c 2 s 1 = 1, is called a Givens matrix, after the name of the numerical analyst Wallace Givens Since one can choose c = cos θ and s = sin θ for some θ, the above Givens matrix can be conveniently denoted by J(i, j, θ)Geometrically, the matrix J(i, j, θ) rotates a pair of coordinate axes (7th unit vector as its xaxis and the jth unit vector as its yaxis) through the givenLim θ → π / 2 1 − Sin θ ( π / 2 − θ ) Cos θ is Equal to Mathematics MCQAny complete revolution θ and θ 2 nπ are therefore coterminal sin θ, therefore, is equal to sin ( θ 2 nπ ) b) (2 n 1) π The odd multiples of π ± π, ±3 π, ±5 π, ±7 π, 2 n 1 (or 2 n − 1) typically signifies an odd number Zeros When we write sin θ, θ




Proved That 2 Sin P 4 Theta Costheta Sintheta Brainly In



List Of Trigonometric Identities
SOLUTION Concept sin (π – θ) = sin θ Calculation Given that A B C = π ⇒ A B = π C Now, sin (A B) sin C = sin (π – C) sin C Explanation LHS =left hand side, RHS =right hand side Use formula cos(A− B) = cosAcosB sinAsinB LHS = cos(π 2)cosθ sin( π 2)sinθ = 0 × cosθ 1 ×sinθSub your expression for \sin (\theta) In the second equation you can use cos(θ)2 = 1− sin(θ)2 and get a quadratic in sin(θ), solve that for sin(θ) in terms of y(θ) Sub your expression for sin(θ) Transform complex exponential integral to real Transform complex exponential integral to real




Value Of Sin 180 Degrees How To Find Sin P Value
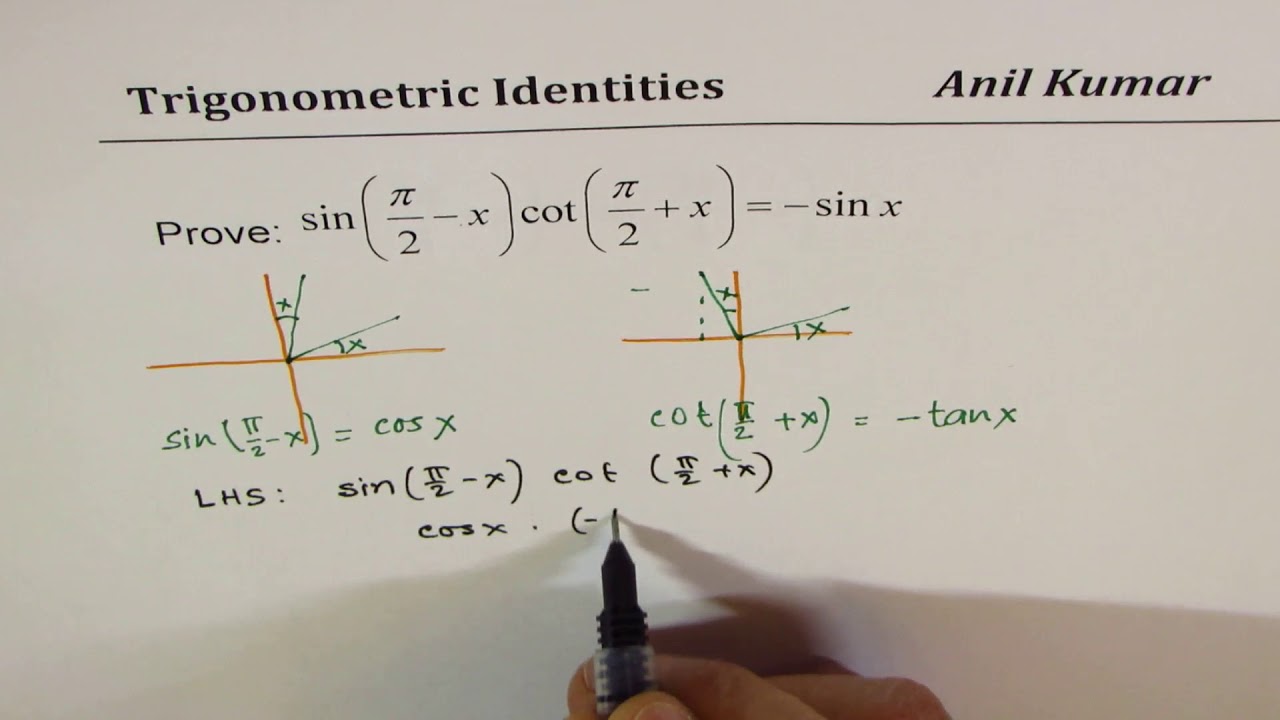



Sin Pi 2 X Cot Pi 2 X Sinx Trigonometric Identities With Related Acute Angle Youtube
The trigonometric R method is a method of rewriting a weighted sum of sines and cosines as a single instance of sine (or cosine) This allows for easier analysis in many cases, as a single instance of a basic trigonometric function is often easier to work with than multiple are The R method is most often used to find the extrema (maximum and minimum) of combinations of trigonometric Find real θ such that (3 2i × sin θ)/(1 – 2i × sin θ) is imaginary (a) θ = nπ ± π/2 where n is an integer (b) θ = nπ ± π/3 where n is an integer (c) θ = nπ ± π/4 where n is an integer (d) None of these Answer Answer (b) θ = nπ ± π/3 where n is an integer Hint Given,This can be seen by solving the equation 3 sin (2 θ) = 0 3 sin (2 θ) = 0 for θ θ Therefore the values θ = 0 θ = 0 to θ = π / 2 θ = π / 2 trace out the first petal of the rose To find the area inside this petal, use Equation 79 with f (θ) = 3 sin (2 θ), f (θ) = 3 sin (2 θ), α = 0, α = 0, and β = π / 2 β = π / 2




Solving Sinusoidal Equations Of The Form Sin X D Video Khan Academy
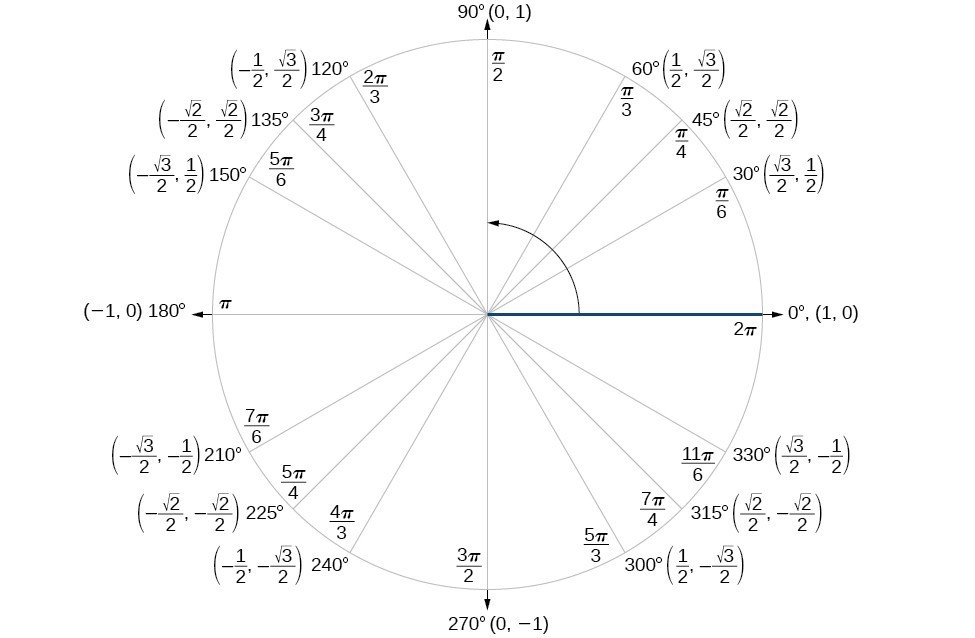



Sum And Difference Identities Precalculus Ii
Sin (π/2theta) = cos theta As π/2theta lies in the second quadrant so the answer will be in positive as it is lying in sin (second quadrant) and because of π/2 the sin will convert into cos theta 12K views Sponsored by AntidotemeConclusion The chart of variations of sinθ vesus θ from 0 to 2π as well as the corresponding graph are shown below Example 1 Verify the following equality sin(90) 2sin(0°) 3sin(180°) 4sin(270) = 5 Solution Always, leave one side untouched, and work on the other side until both sides prove to be equal In this example, the left side can be worked on;Sin1 sin 5 π 6 = sin1 sin π π 6 ∵ sin π θ = sin θ = sin1 sin π 6 ∵ Principal value ∈ 0, π 2 = π 6 which is the required principal value Answer




Show The Trig Identity Sin Pi 2 Theta Cos Theta Youtube



Graphs Of Trigonometric Functions




Trigonometric Functions Introduction Sine Cosine Videos And Examples




Sin P 2 8 Cos 8 Youtube




Is It Possible To Express Sin Frac Pi 9 In Terms Of Radicals Mathematics Stack Exchange



Biomath Trigonometric Functions




In Cofunction Identity Sin 3 P 2 8 Is Equ Gauthmath



Assignment 1 Exploring Sine Curves



1



The Trigonometric Ratios Of Angl




Easy Way Of Memorizing Values Of Sine Cosine And Tangent Mathematics Stack Exchange




Why Sin N Pi 0 And Cos N Pi 1 N Mathematics Stack Exchange




Content Graphing The Trigonometric Functions
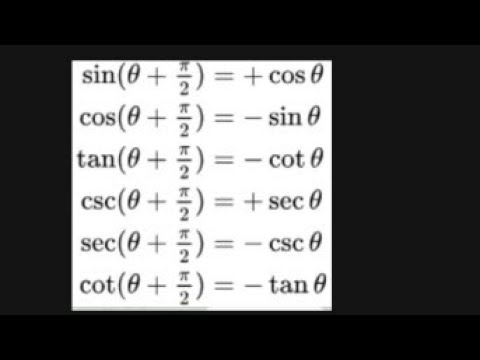



Proof Of Sin P 2 8 Cos8 Upto Cosec P 2 8 Sec8 Using Euler S Formula Youtube




The Value Of T A Nthetasin Pi 2 Theta Cos Pi 2 Theta Is 1 B 1 C 1 2sin2theta D None Of These
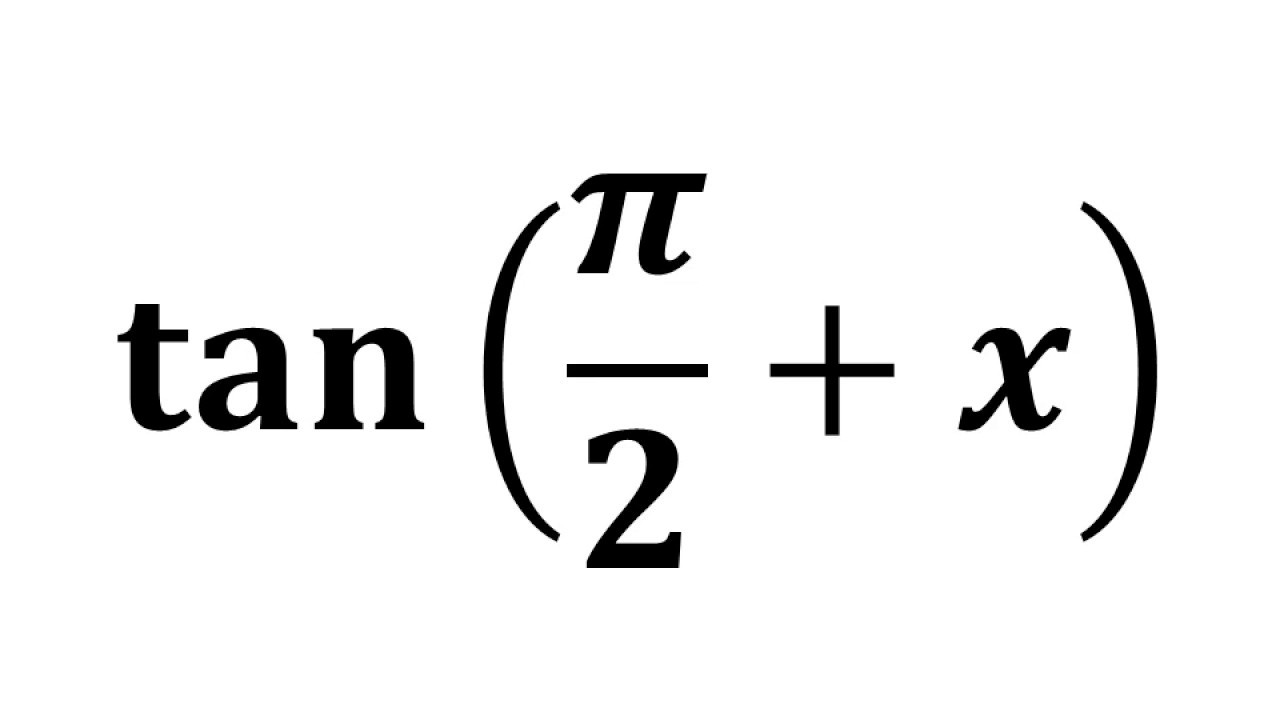



Tan Pi 2 X Tan Pi 2 Theta Youtube




Integration With Lim Pi 2 To 0 Of Sin2theta Sin Theta Dtheta Pi N Then Find N Maths Integrals Meritnation Com



Sine Cosine Identities Periodicity Video Khan Academy
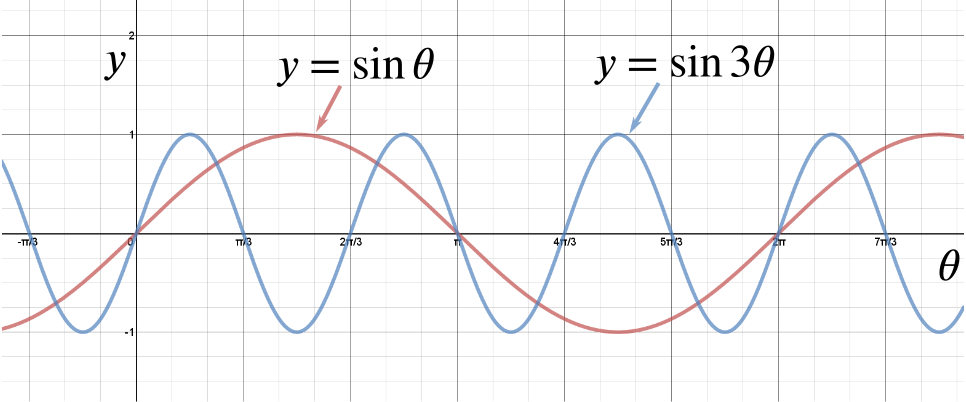



Solution When Is Sin Theta Sin 3 Theta Trigonometry Compound Angles Underground Mathematics



The Trigonometric Ratios Of Angl



List Of Trigonometric Identities



The Trigonometric Ratios Of Angl
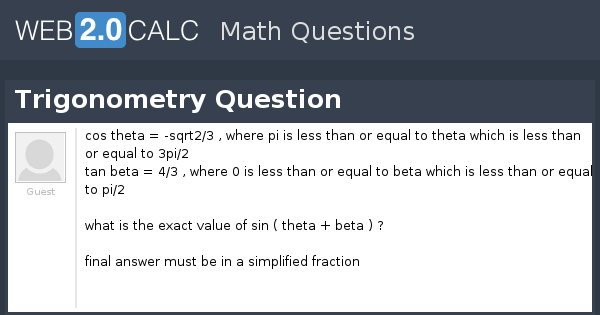



View Question Trigonometry Question



List Of Trigonometric Identities



The Trigonometric Ratios Of Angl



1



Inverse Trigonometric Functions Precalculus Ii
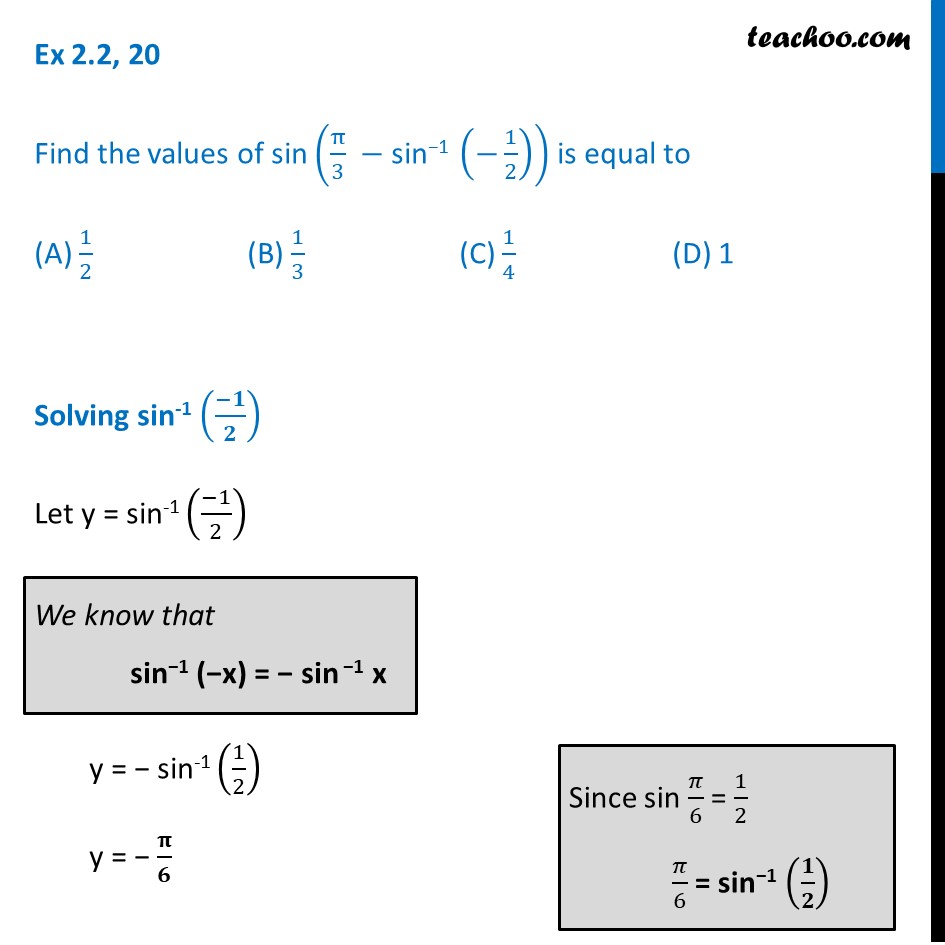



Ex 2 2 Mcq Find Sin Pi 3 Sin 1 1 2 Class 12 Ncert
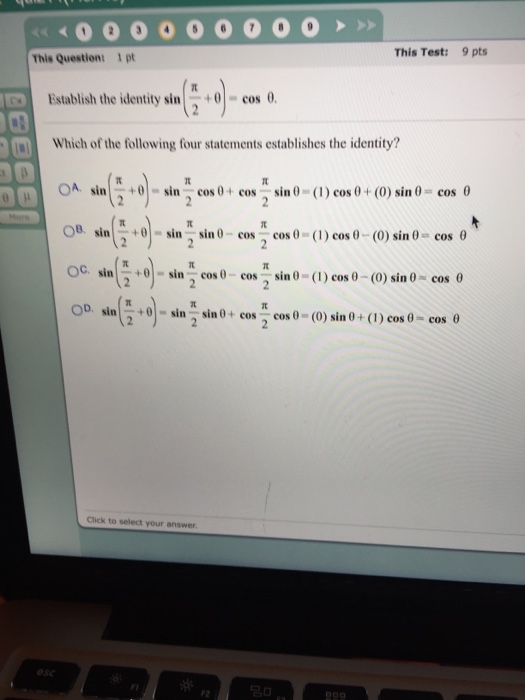



Establish The Identity Sin Pi 2 Theta Cos Theta Chegg Com
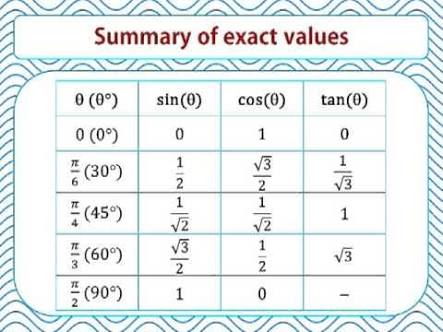



What Is Sin 2pi 3 Equal To Socratic



The Trigonometric Ratios Of Angl



Prove That Sin P X Cos P 2 X Tan 3p 2 X Cot 2p X Sin 2p X Cos 2p X Cosec X Sin 3p 2 X 1 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




Trigonometry Angles Pi 2 From Wolfram Mathworld



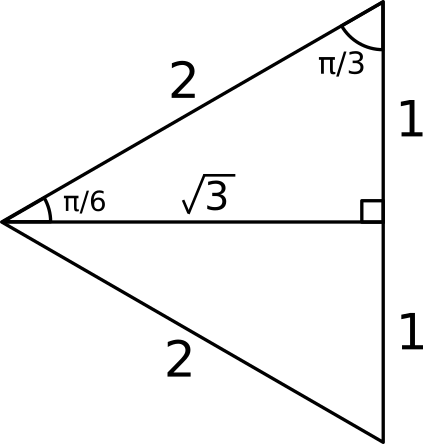
How Do You Simplify Sin Pi 3 Socratic



Cos Pi 2



List Of Trigonometric Identities




If Theta In Pi 2 3 Pi 2 Then Sin 1 Sin Theta Equals




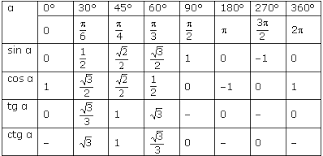
त र क णम त य सर वसम क ओ क स च व क प ड य
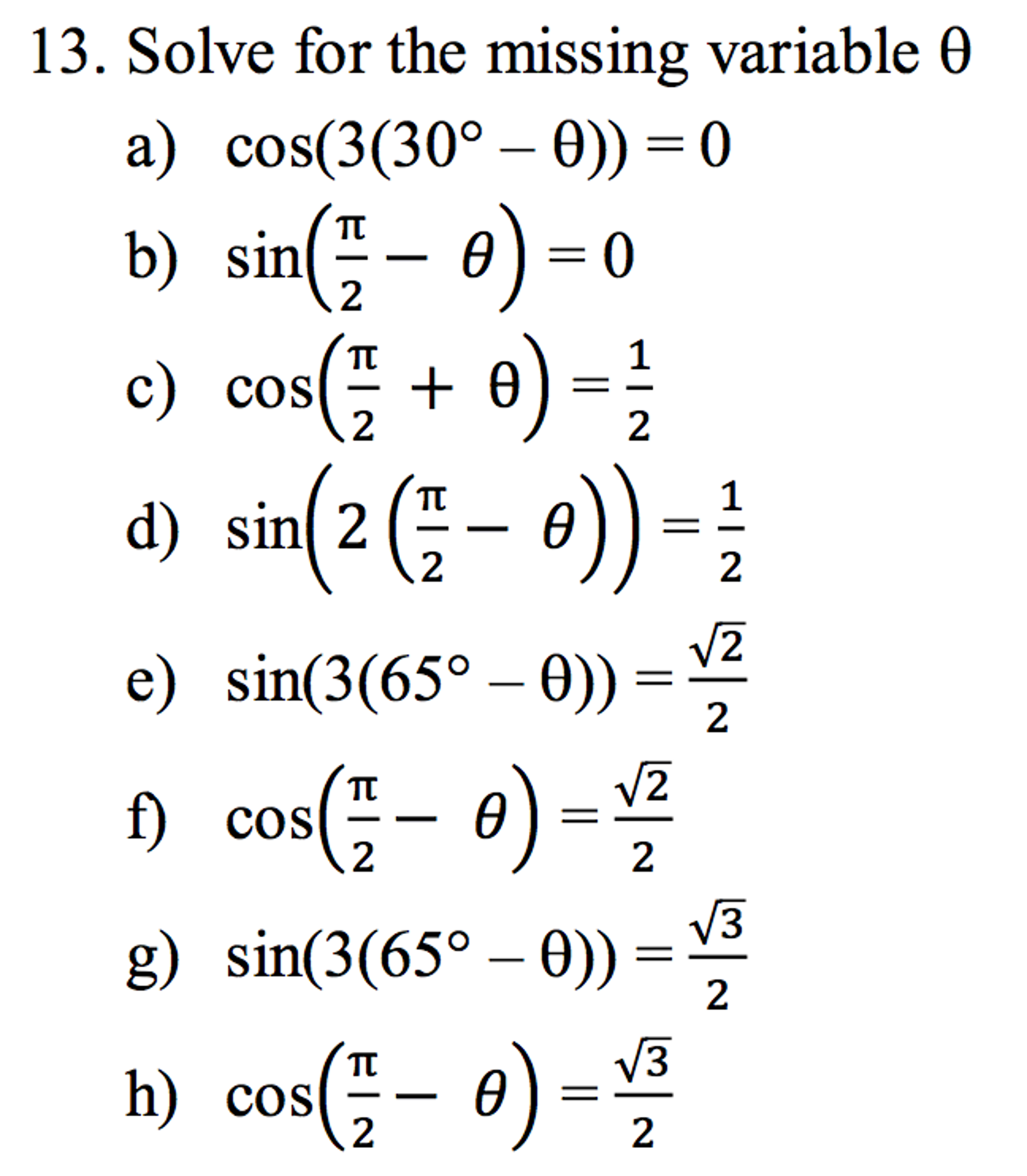



Solve For The Missing Variable Theta Cos 3 30 Degree Chegg Com



What Is The Value Of Sin P 2 Theta Quora




Content Graphing The Trigonometric Functions



The Trigonometric Ratios Of Angl




Trigonometric Functions Of Allied Angles Sin Pi Theta Sin Theta Cos Pi Theta Cos Theta Tan Pi Theta Tan Theta Sin 2 Pi Theta Sin Theta Cos 2 Pi Theta Cos Theta Tan 2 Pi Theta Tan Theta Sin Left Frac 3



How To Simply Prove That Cos P 2 X Sinx Quora



The Trigonometric Ratios Of Angl



What Is The Value Of Sin 2 Pi 2 Cos Pi Socratic



Exact Trig Values




Content Graphing The Trigonometric Functions



Sin T Cos Pi 2 T Wolfram Demonstrations Project




Prove Cos X Pi 2 Sinx Youtube
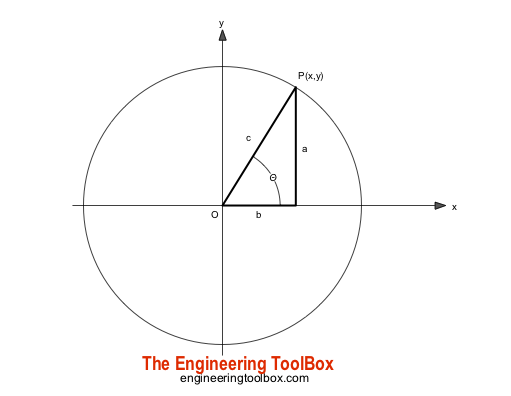



Trigonometric Functions



1
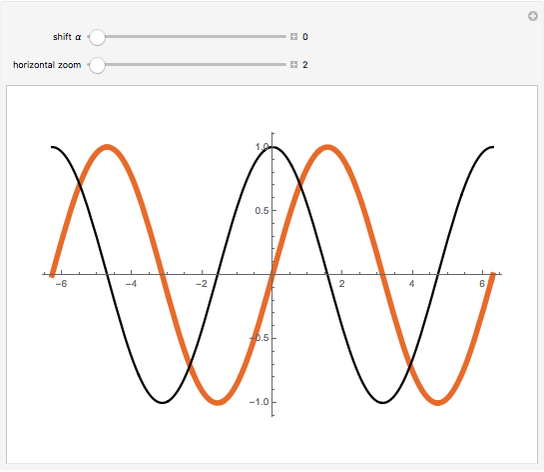



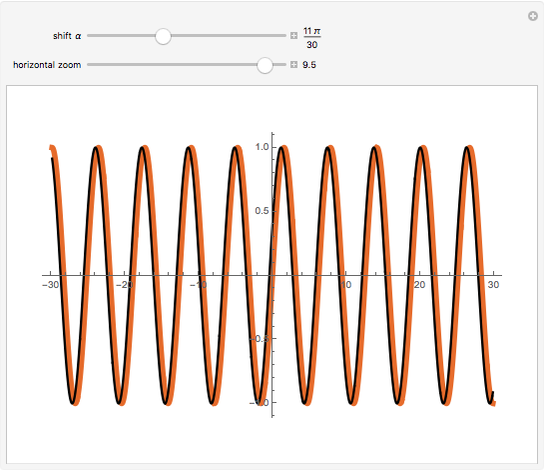
Sin T Cos Pi 2 T Wolfram Demonstrations Project




What Is Sin Of P T When Sin T 4 5 Can You Explain What Sin P T Means Here Quora




Show That Int 0 Pi 2 Sin P Theta Cos Q Theta D Theta Frac Sqrt Frac P 1 2 Sqrt Frac Q 1 2 2 Sqrt Frac P Q 2 2 P Q 1 Mathematics Stack Exchange




List Of Trigonometric Identities Wikipedia
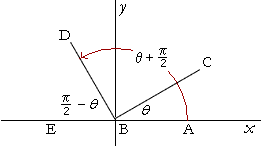



Graphs Of Trigonometric Functions



Signs Of Trigonometric Functions
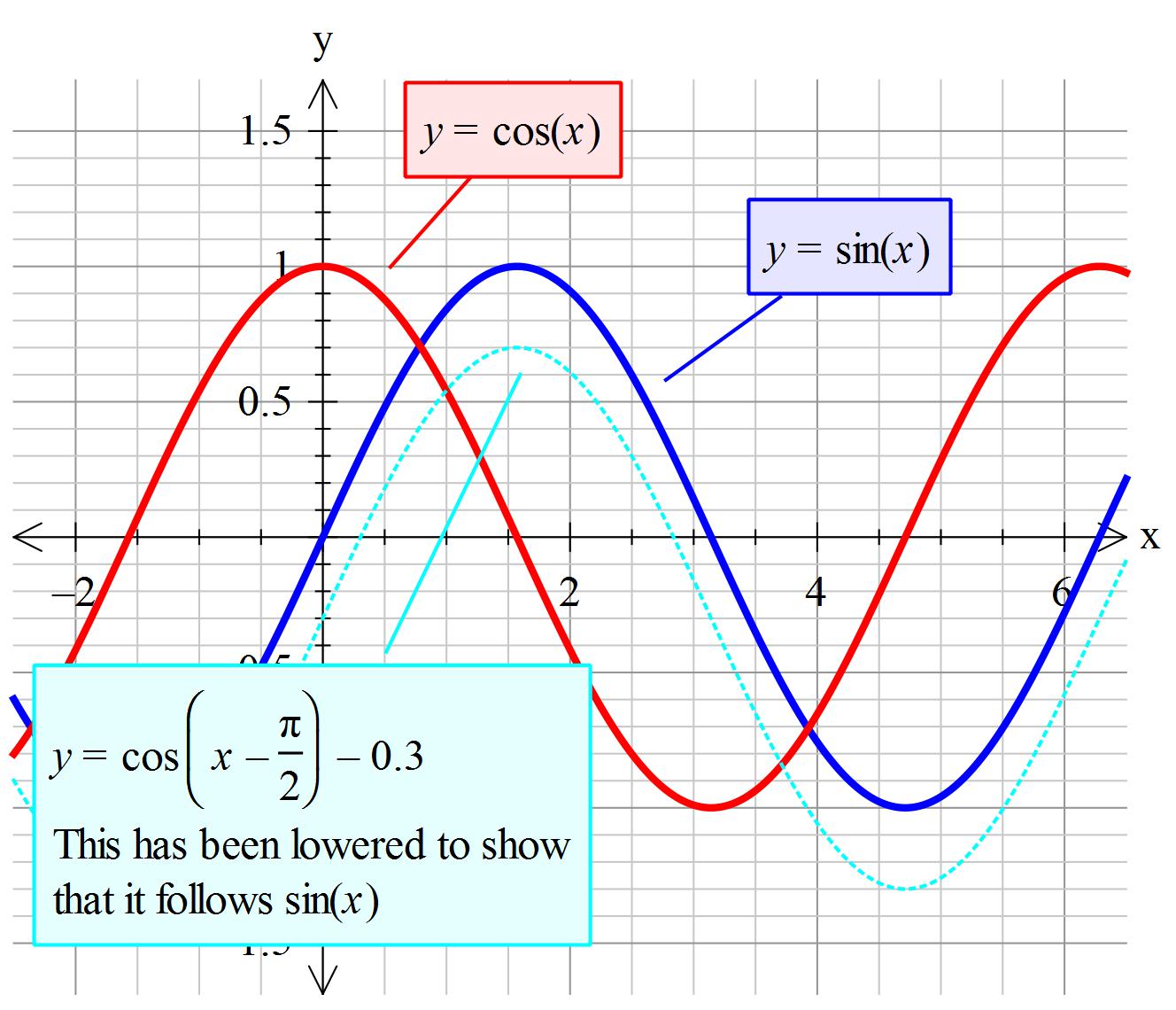



How Do You Prove Cos X Pi 2 Sin X Socratic




Content Graphing The Trigonometric Functions



Trigonometric Functions




What Is The Value Of Math Cos N Pi 2 Math Quora
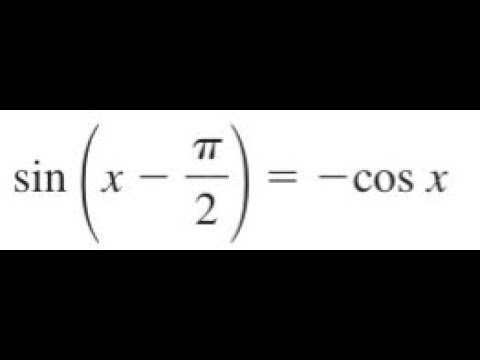



Prove Sin X Pi 2 Cosx Youtube




Trig Challenge Problem Multiple Constraints Video Khan Academy




Proof That Cos Theta Sin Pi 2 Theta Mathematics Stack Exchange



Graph Sine And Cosine Functions
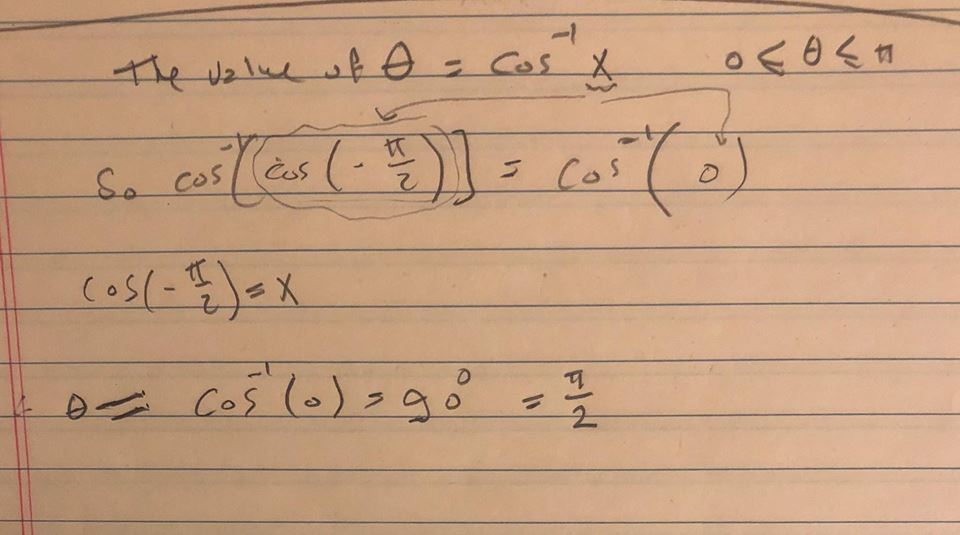



How Do You Evaluate Cos 1 Cos Pi 2 Socratic
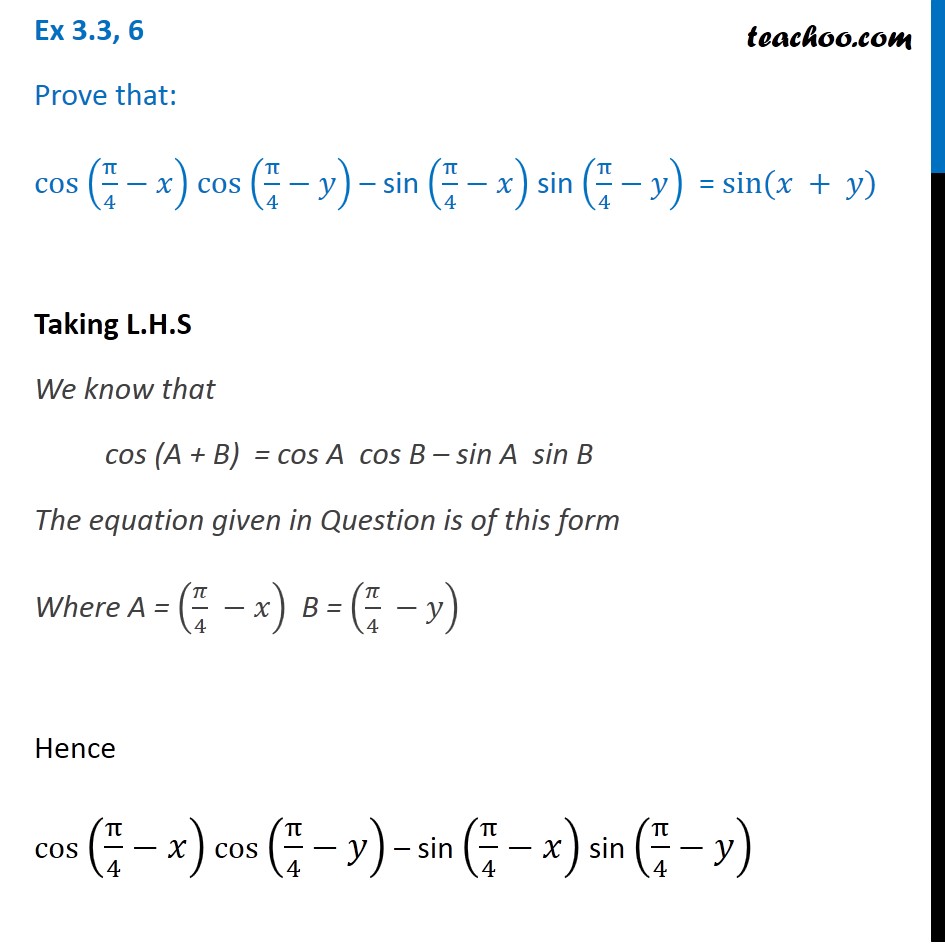



Ex 3 3 6 Prove That Cos Pi 4 X Cos Pi 4 Y Chapter 3




Trigonometric Functions Wikipedia



Biomath Trigonometric Functions
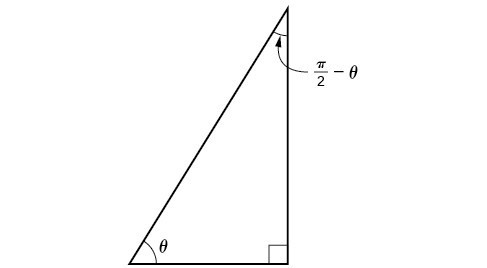



Sum And Difference Identities Precalculus Ii




Trigonometric Functions
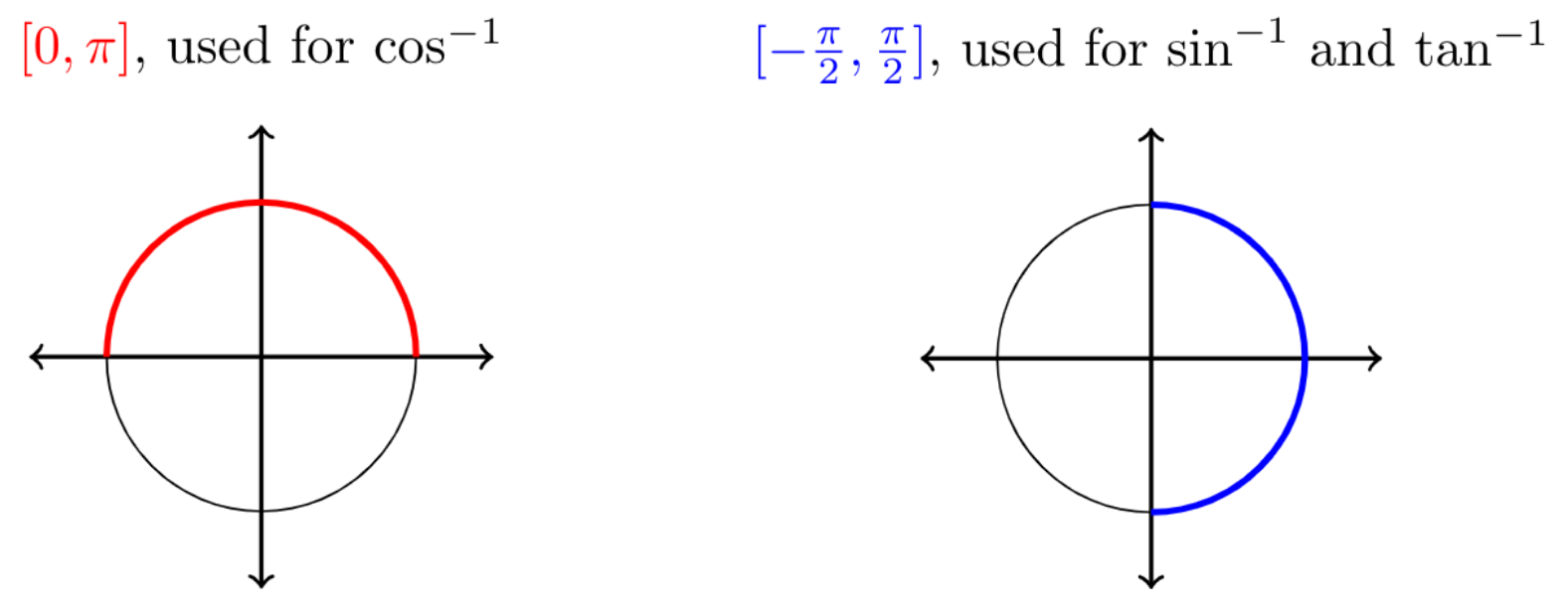



Mfg Inverse Trigonometric Functions




Cos Pi 2




General Solution To The Eqation 2 Theta Cos 2 Theta 1 0 Will Be Given By A Sqrt Theta Mathbf
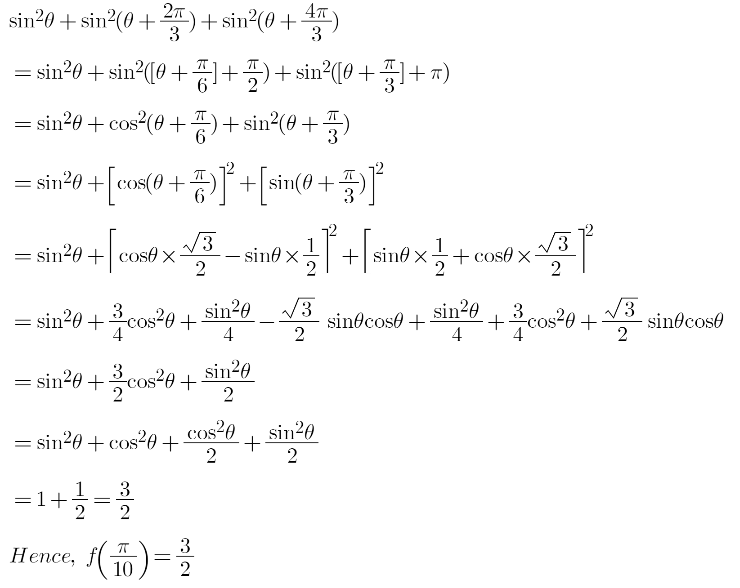



If F Theta Sin2 Theta Sin2 Theta 2 Pi 3 Sin2 Theta 4 Pi 3 Then What Will Bef Pi 10 Mathematics Topperlearning Com Xts72mzz




Trigonometry




Cos 2pi Theta Cosec 2 Pi Theta Tan Pi 2 Theta Sec Pi 2 Maths Trigonometric Functions Meritnation Com



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿