Given f (x) = 3x 2 – x 4, find the simplified form of the following expression, and evaluate at h = 0 This isn't really a functionsoperations question, but something like this often arises in the functionsoperations contextMath Input NEW Use textbook math notation to enter your math Try it8) Apply FOIL in multiplying binomials Multiply the First terms, next is the Outer terms, then the Inner terms, and lastly, the Last terms = tan(x³) 8 tan(x) 2x²/x 2(8)/x Simplifying we get = tan(x³) 8 tan(x) 2x 16/x Now Multiplying it by x to remove the variable in the denominator and we get

F X X2 What Is G X F X G X 2 2 15 Brainly Com
If f(x)=x^2 what is g(x)
If f(x)=x^2 what is g(x)-MPN what people don't see MyMPNteam is a community providing education and resources about MPN , knows a bit of maths A So we have f ( x) = 2 x 1 and g ( x) = x 2 − 2 That basically means that whatever the value of x, f ( x) = 2 x 1 Specifically, if x = g ( − 1), f ( g ( − 1)) = 2 gSimple and best practice solution for g(x)=f(x2) equation Check how easy it is, and learn it for the future Our solution is simple, and easy to understand,



Manipulating Graphs
Wronskian({f(x), g(x), h(x)}, x) Natural Language;G(f (x)) g ( f ( x)) Evaluate g(f (x)) g ( f ( x)) by substituting in the value of f f into g g g(x−2) = (x−2)2 g ( x 2) = ( x 2) 2 Combine the opposite terms in (x− 2)2 ( x 2) 2 Tap for more steps Add − 2 2 and 2 2 g ( x − 2) = x 0 g ( x 2) = x 0 Add x x and 0 0 g ( x − 2) = x g ( xWhat point is on the graph f?
Transcribed image text Given that f(x) = X^2 2x 3, find the value(s) for x such that f(x) = 11 Given the (f g)(x) = 4x 4/x(x 4) and f(x) = 5/x 4, find g(x) Given that f(x) = x 1/x^2 4, a) Find the domain of f (b) Is the point (1, 2/3) on the graph of f?G(x) = 2x 1 (f g) (x) = fF (x) = x2 − 4 f ( x) = x 2 4 ;
The Chain Rule says the derivative of f (g (x)) = f' (g (x))g' (x) The individual derivatives are f' (g) = cos (g) g' (x) = 2x So d dx sin (x 2) = cos (g (x)) (2x) = 2x cos (x 2) Another way of writing the Chain Rule is dy dx = dy du du dxComposite Function A composite function is a function which is made by combining two or more than two functions For example, if {eq}f(x) {/eq} and {eq}g(xOr the value of the function evaluated at 2x Giving a name f to a function for the function using independant variable x will be named as f (x), to be read, the function f of x Shown alone, f and x are not factors, but are a complete name




Verifying Inverse Functions By Composition Not Inverse Video Khan Academy




Function Transformations Algebra Ii Quiz Quizizz
Learn how to solve f(g(x)) by replacing the x found in the outside function f(x) by g(x)F (g (2)), g (x)=2x1, f (x)=x^2 \square!Ex 13, 6 Show that f −1, 1 → R, given by f(x) = 𝑥/(𝑥 2) is oneone Find the inverse of the function f −1, 1 → Range f (Hint For y ∈ Range
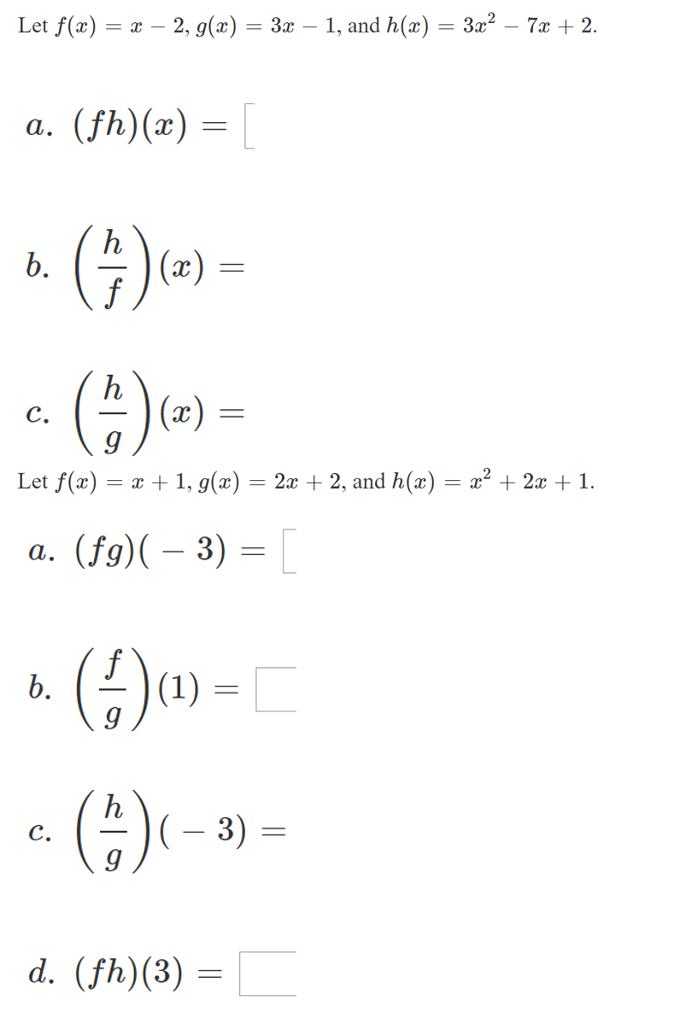



Let F X X 2 G X 3x 1 And H X 3x 2 7x Chegg Com




View Question Please Help
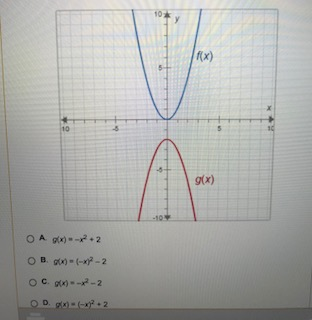
Vertical Translation For the base function f (x) and a constant k, the function given by g (x) = f (x) k, can be sketched by shifting f (x) k units vertically Horizontal Translation For the base function f (x) and a constant k, the function given by g(x) = f (x k), can be sketched by shifting f (x) k units horizontally Vertical Stretches and ShrinksLet f_1(x)=x^2 Then f_1'(x)=2x<0 and g_1(x)=x^2(1x))^2 = 2x^22x1 and g_1'(x)=24x so g(x) is decreasing when x>\frac{1}{2} On the other hand, if f_2(x)=(1x)^2 Then f_2'(x)=2(1x1 Answer AJ Speller (f ∘ g)(x) = f (g(x)) = f (x 2) = (x 2)2 Click on the link below to see another example If f (x) = x2 and g(x) = x 2, what is (g ∘ f)(x)?




Let F Be The Function Defined By F X X 3 X If G X Is The Inverse Of F X And G 2 1 What Is The Value Of The Derivative Of G At X 2




If F X 2x And G X X 2 2 1 Then Which Of The Following Can Be Discontinuous Function Youtube
Whenever G(x) = 0 then the You can view more similar questions or ask aF (x)=2x3,\g (x)=x^25,\f (g (x)) f (x)=2x3,\g (x)=x^25,\f\circ \g f (x)=2x3,\g (x)=x^25,\ (f\circ \g) (2) functioncompositioncalculator f (x)=2x3, g (x)=x^25, f (g (x)) enF(3) = g(3) hich represents where f(x) = g(x)?




F X X2 What Is G X 1 16 Brainly Com
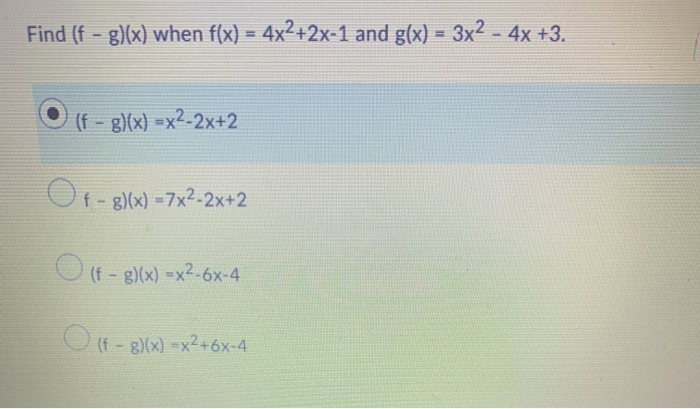



Find F G X When F X 4x2 2x 1 And G X 3x2 Chegg Com
Solve your math problems using our free math solver with stepbystep solutions Our math solver supports basic math, prealgebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and moreThe function f(x) = 3x^2 x 2 To determine the value of f(x) for different values of x, substitute for x in the expression of the function and simplifyF(4) = g(4) and f(0) = g(0)




F X X 2 What Is G X Brainly Com
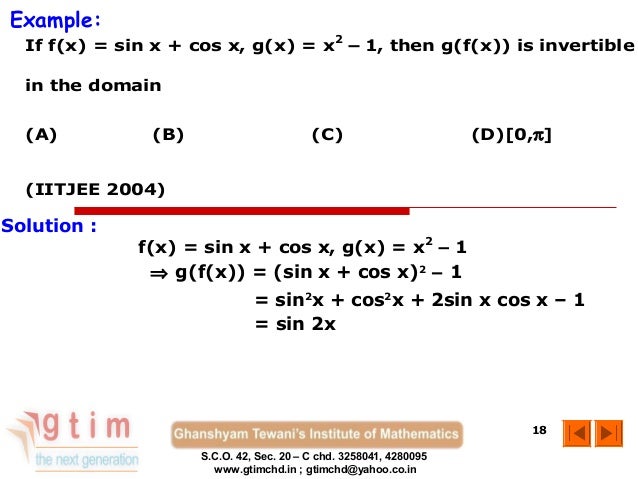



Composite Functions
For example, if we apply the function f to f(x), we have ff(x) or f 2 (x) f 2 (x) = ff(x) = f(x 3) = (x 3) 3 = x 9 One thing to note when calculating composite functions is that fg(x) is unlikely to be the same as gf(x) For instance, from using f(x) and g(x) from our example above, we can calculate gf(xExplanation substitute g(x) = 4x −1 into f (x) ⇒ f (4x −1) = (4x −1)2 3(4x − 1) = 16x2 −8x 1 12x − 3 = 16x2 4x −2 ⇒ (f ∘ g)(x) = 16x2 4x −2 to evaluate (f ∘ g)(0) substitute x = 0 into (f ∘ g)(x)The functions are combined to form the new functions h(x) = f(x) g(x) and j(x) = f(x) g(x) Point (6, 2) is in the function h(x), while the point (2, 10) is in the function Simpson's rule Is the simpson's rule always more accurate than the midpoint rule and trapezoidal rule?



Secure Media Collegeboard Org Digitalservices Pdf Ap Apcentral Ap15 Calculus Ab Q2 Pdf
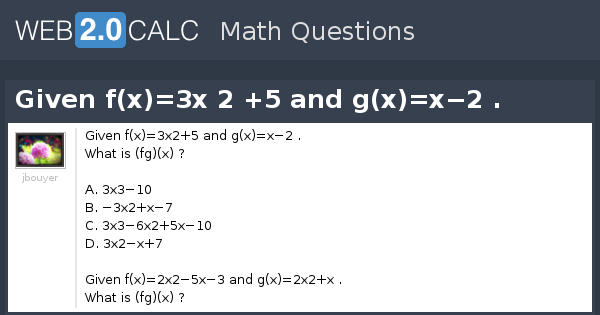



View Question Given F X 3x 2 5 And G X X 2
(c) If x = 3, what is f(x)?Knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students &Inverse Functions Inverse functions are functions that undo one another In other words, if f1 (x) is the inverse of f(x), then f(f1 (x)) = f1 (f(x)) = xWe can use this definition to solve
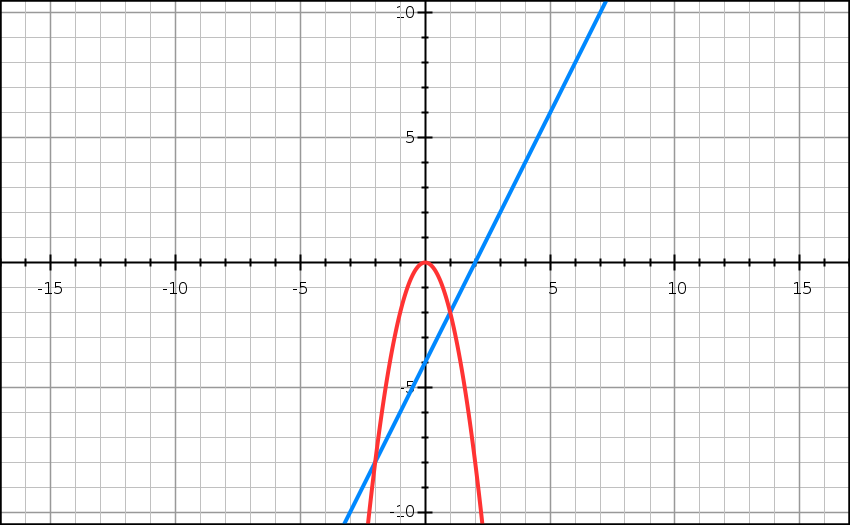



How Do You Draw F X 2x 2 And G X 2x 4 On The Same Graphs Socratic
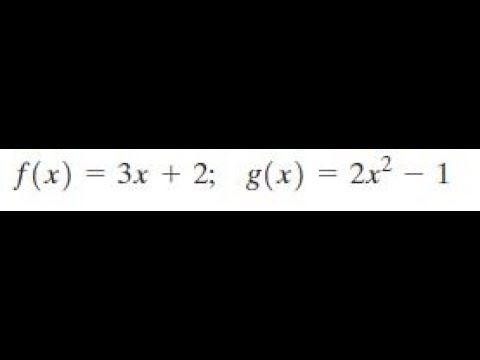



F X 3x 2 G X 2x 2 1 Youtube
And ( f o g)(x) means f (g(x)) That is, you plug something in for x, then you plug that value into g, simplify, and then plug the result into f The process here is just like what we saw on the previous page, except that now we will be using formulas to find values, rather than just reading the values from lists of points Given f(x) = 2xGiven f(x) = 23x Replace x with g(x) f(g(x)) = 2–3(x1) Simplify f(g(x))= 23x3 f(g(x))=53x QED= 2x 3 x 2 2 The domain of (f g)(x) consists of all xvalues that are in the domain of both f and g In this example, f and g both have domain consisting of all real numbers, therefore (f g)(x) also has domain consisting of all real numbers The Difference of Two Functions
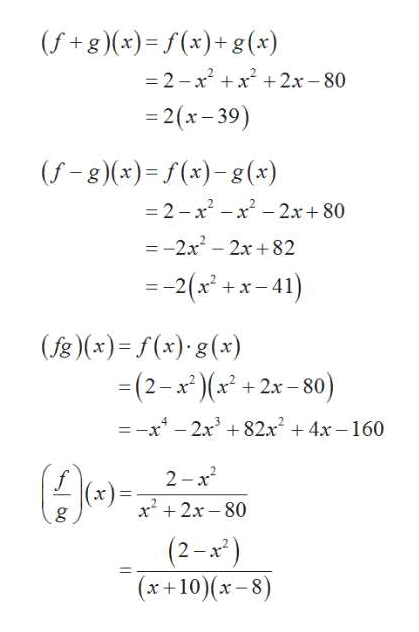



Answered For The Functions F X 2 X2 And G X X2 Bartleby




Suppose That We Have Two Functions F X And G X Chegg Com
If the domain of a function F is the set of all real numbers and the domain of a function G is the set of all real numbers, under what circumstances do (FG)(x) and (F/G)(x) have different domains?1,034 272 #2 the letter which you use to label a function has no special meaning g (x) just identifies a function of x, in the same way as that f (x) does Using a g instead of an f only means the function has a different label assigned to it Typically this is done where you have already got an f (x), so creating another one would be confusingSecond component * derivative of the first component Step 3 Now add those two together xf' (x)f (x) to arrive at g' (x)=xf' (x)f (x) Yet another way to remember it first times the derivative of the second second times the derivative of the first



Www Manhassetschools Org Site Handlers Filedownload Ashx Moduleinstanceid 4085 Dataid Filename Aimm 27 with key Pdf
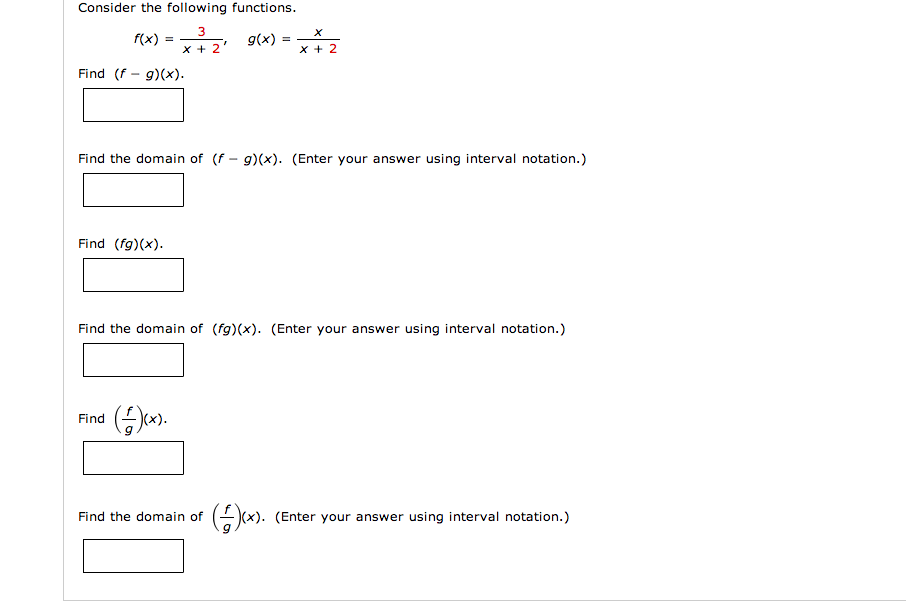



Consider The Following Functions F X 3 X 2 Chegg Com
The composite functions of higher math often use h(x) and g(x), in combination,,defining which comes first, and which is second The substitution is bad enough, but using y's would make it worse In summary, feel free to immediately use y = instead of h(x), if it clarified the problemStep1 x*f' (x) ==>Therefore, let f(x) = g(x) = 2x 1 Then, f(x)g(x) = 4x 2 4x 1 = 1 Thus deg(f⋅g) = 0 which is not greater than the degrees of f and g (which each had degree 1) Since the norm function is not defined for the zero element of the ring, we consider the degree of the polynomial f(x) = 0 to also be undefined so that it follows the rules of a




F X X 2 What Is G X Brainly Com



F X X 2 What Is G X 1 9
First component * derivative of the second component Step 2 f (x) * 1 ==>F(x)=x 4 −x 2 9 g(x)=x 3 3x 2 12 2 What is (f⋅g)(x)?Professionals For math, science, nutrition, history, geography, engineering, mathematics, linguistics, sports, finance, music




Misc 15 Let F X X2 X G X 2 X 1 2 1 Are F G




Function Composition Given F X 2x 2 And G X 2 Find F ºg X F ºg X F G X Start On The Inside F G X G X 2 So Replace It F G X F 2 Ppt
Find (f g)(x) for f and g below f(x) = 3x 4 (6) g(x) = x2 1 x (7) When composing functions we always read from right to left So, rst, we will plug x into g (which is already done) and then g into f What this means, is that wherever we see an x in f we will plug in g That is, g acts as our new variable and we have f(g(x)) 12*f (x) means two multiplied by the function f f (2x) means the function at 2x;B (1/4x)^2 will widen the parabola C 4x^2 is too wide to be g(x) D (16x)^2 is too narrow to be g(x) A is the correct answer When graphed on desmos com / calculator it shows this is the correct answer I hope this helped!



Are Inverses F X




F X X 2 What Is G X A G X X 2 4 B G X X 2 4 C G X 4x 2 D G X X 2 4 Brainly Com
Extended Keyboard Examples Upload Random Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology &G(x) = 2x 1 g ( x) = 2 x 1 Set up the composite result function f (g(x)) f ( g ( x)) Evaluate f (g(x)) f ( g ( x)) by substituting in the value of g g into f f f (2x1) = (2x1)2 − 4 f ( 2 x 1) = ( 2 x 1) 2 4 Simplify each term Tap for more steps Rewrite ( 2 x 1) 2 ( 2 x 1) 2 as ( 2 xF(x)=x 2 2x−6 g(x)=x 4 3 3 jbouyer




F X X 2 What Is G X Brainly Com




Please Help F X X 2 What Is G X Brainly Com
Odd functions If f ( x) is an odd function, then for every x and − x in the domain of f, − f ( x) = f ( − x) Graphically, this means that the function is rotationally symmetric with respect to the origin Thus, rotations of 180 ∘ or any multiple of 180 ∘ do not affect the function's appearance Good examples of odd functionsAs an example, a classic result of Ritt shows that permutable polynomials are, up to a linear homeomorphism, either both powers of x, both iterates of the same polynomial, or both Chebychev polynomials We say f and g commute (with respect to composition) The property is called commutativitySOLUTION Find (fg) (x), (fg) (x), (f*g) (x) and (f/g) (x) for each f (x) and g (x) 2 f (x)= 8x^2 g (x)=1/x^2 I'm having trouble understanding what i have to do, please help You can put this solution on YOUR website!




F X X2 What Is G X Brainly Com




Find The Greatest Common Divisor Of F X 2x 3 2x 2 X 4 And G X X 4 3x 3 4x 2 3x Mathematics Stack Exchange
Get stepbystep solutions from expert tutors as fast as 1530 minutes Your first 5 questions are on us!(d) If f(x) = 2, find the value(s) of xFor f(x) = x 4/x 7 and g(x) = x 2/x 3, find the following composite functions and state the domain of each f g g f f f g g What is the domain of f f Domain {xx 7, x 45/8} (Use integers or fractions for any numbers in the expression) (g g(x) = 3x 4/2x 11 (Factor completely




F X X 2 What Is G X Brainly Com



If F X 3x 2 4 And G X X 2 Find F G X Chegg Com
I'll give you a hint to get you started IfGiven F(x) = 4x2 6x and g(x) = 2x2 13x 15, find (f/g) (x) please show work i really dont understand this1 What is (f−g)(x)?




F X X2 What Is G X F X G X 2 2 15 Brainly Com



What Is The Continuity Of The Composite Function F G X Given F X Sinx And G X X 2 Socratic
Which statement is true regarding the functions on the graph?Example 16 Let f(x) = x2and g(x) = 2x 1 be two real functions Find (f g) (x), (f – g) (x), (fg) (x), (f /𝑔) (x) f(x) = x2 &It is possible that the midpoint and/or




F X X 2 What Is G X Brainly Com




Consider The Following Functions F X X 2 G X Chegg Com
In this video we learn about function composition Composite functions are combinations of more than one function In this video we learn about f(g(x)) and gSimple and best practice solution for g(x)=f(1/3x) equation Check how easy it is, and learn it for the future Our solution is simple, and easy to understand,Replace the x in the f(x) equation with the value of g(x) to get (x3)cubed 2That's it When you write f(x) = x3 2 That means x can be any number, equation or function and whatever that value is, it goes into x3 2
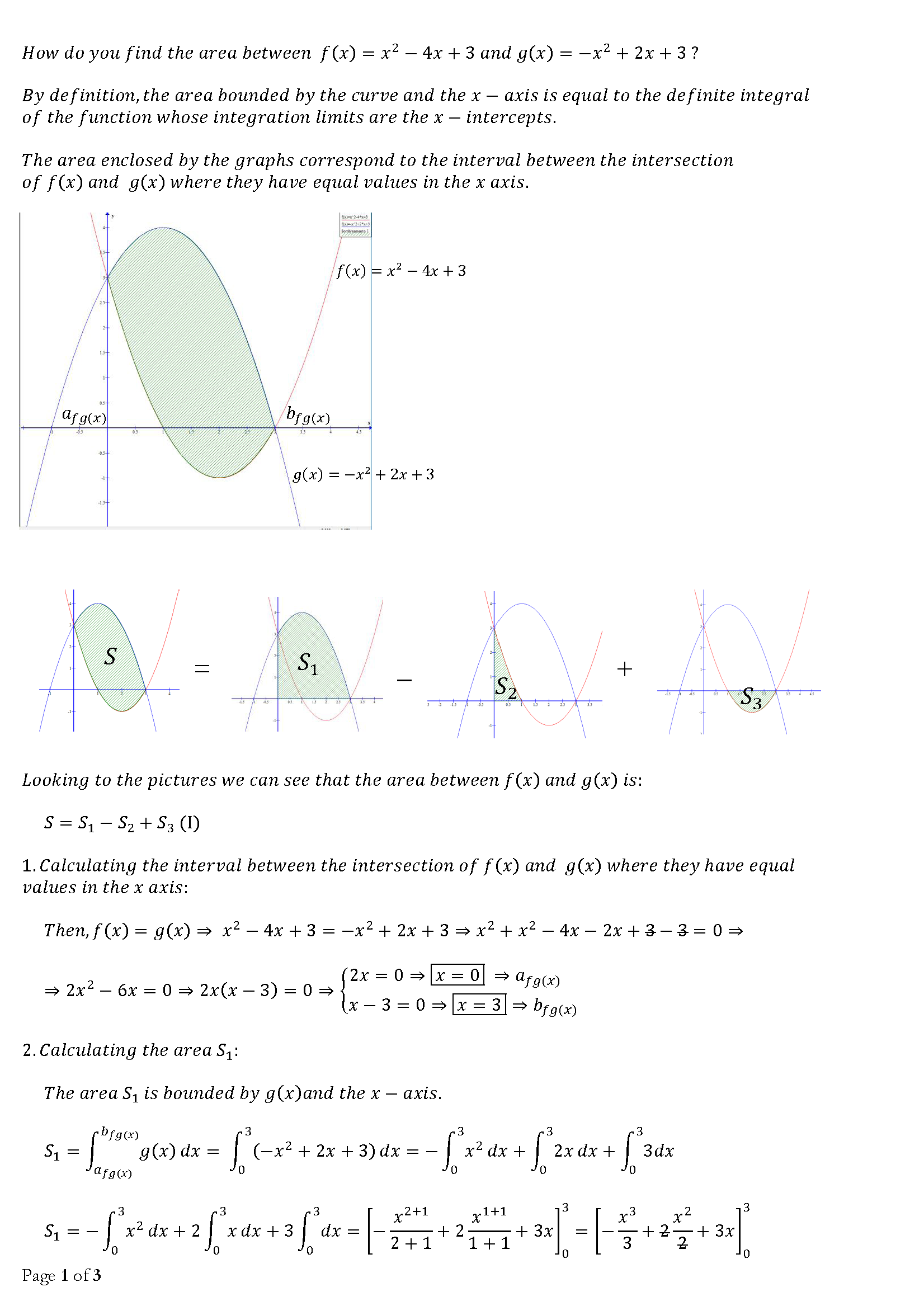



How Do You Find The Area Between F X X 2 4x 3 And G X X 2 2x 3 Socratic




Please Help Me F X X2 What Is G X Brainly Com
F(x)*g(x) = (tan(x) 2/x)(x²




F X X 2 What Is G X Brainly Com




F X X 2 What Is G X Brainly Com



Www3 Nd Edu Apilking Math Work Old exams Exam1f08soluutions Pdf



1 3 Let F X X2 7 And G X X 3 Find The Chegg Com




Find The Following F X 2x 3 G X 2 X F Chegg Com




7 If F X And G X X2 2x Find Fg X And Its Chegg Com



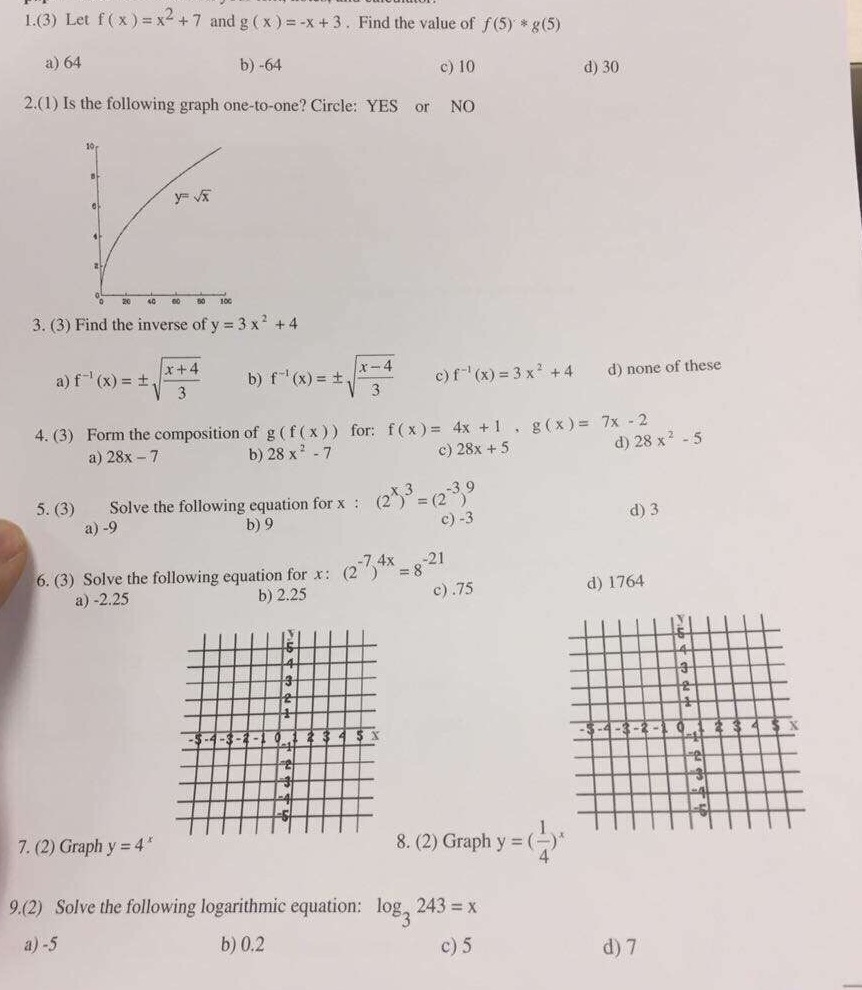
The Functions F X And G X Are Shown On The Graph Chegg Com




If F G X 4x2 8x And F X X2 4 Then G X A 4 Maths Relations And Functions Meritnation Com




If F X X 2 And G X 2x Then Evaluate I F G 3 Ii F G 2 Iii F G 1 Iv F G 5




F X X2 What Is G X Brainly Com




F X X 2 What Is G X Brainly Com



Efisd Net Common Pages Displayfile Aspx Itemid




If F X 3x 2 And G X X 2 Then Fog X Youtube



How Do You Find The Area Between F X X 2 2x 1 G X 3x 3 Socratic




J J Allu G X El 4 Let F X X And G X 3x Chegg Com



Question Video Finding The Composite Of Two Functions Nagwa



Suppose F X X 2 What Is The Graph Of G X F 3x
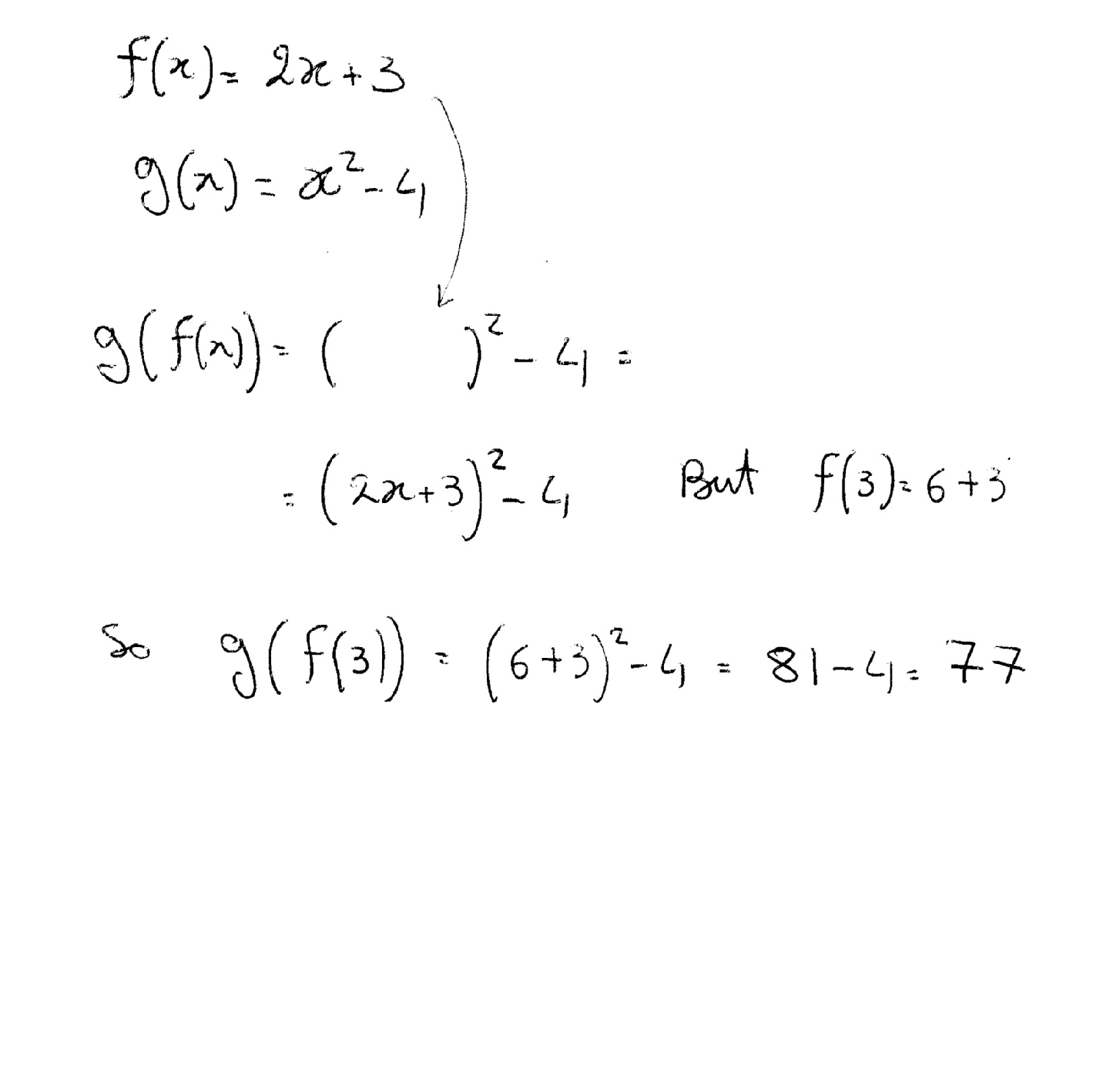



Let F X 2x 3 And G X X 2 4 And H X X 3 2 How Do You Find G F 3 Socratic
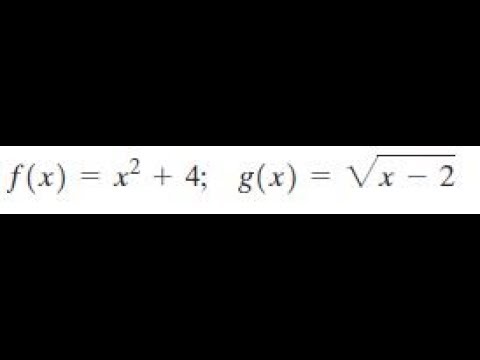



F X X 2 4 G X Sqrt X 2 Youtube
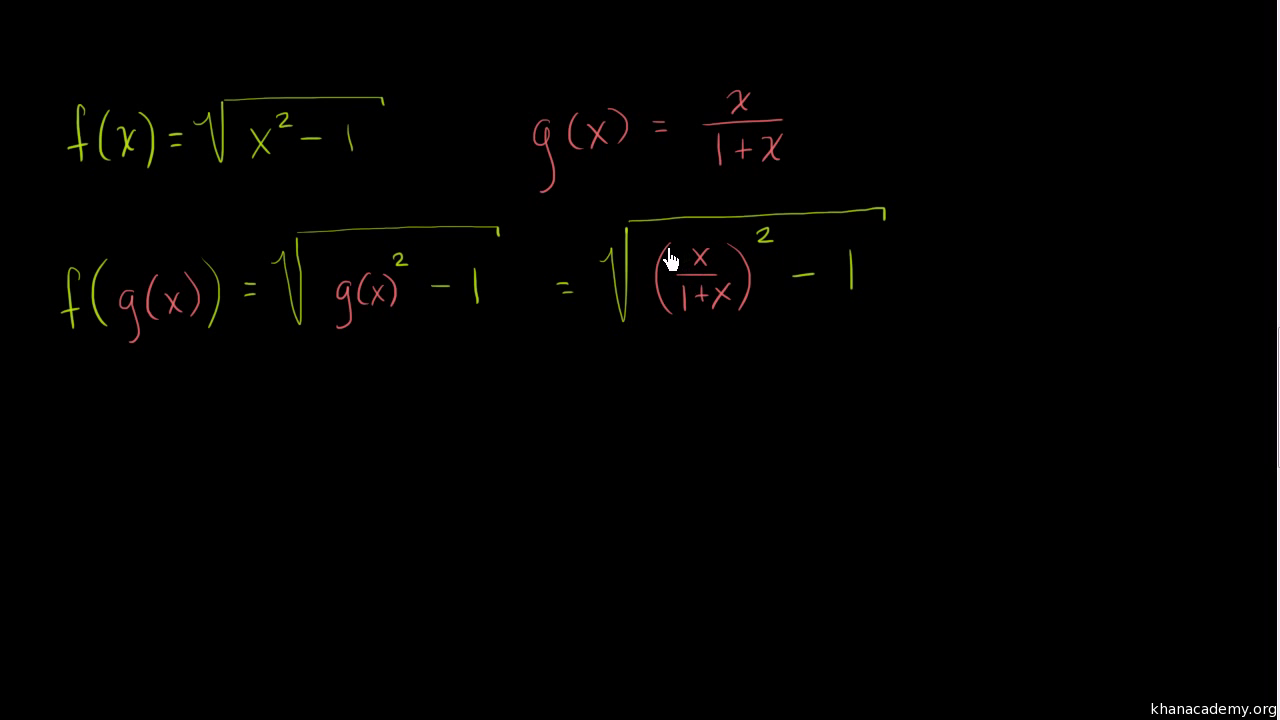



Finding Composite Functions Video Khan Academy




Please Help Suppose F X X 2 What Is The Graph Of G X 1 4 F X Brainly Com
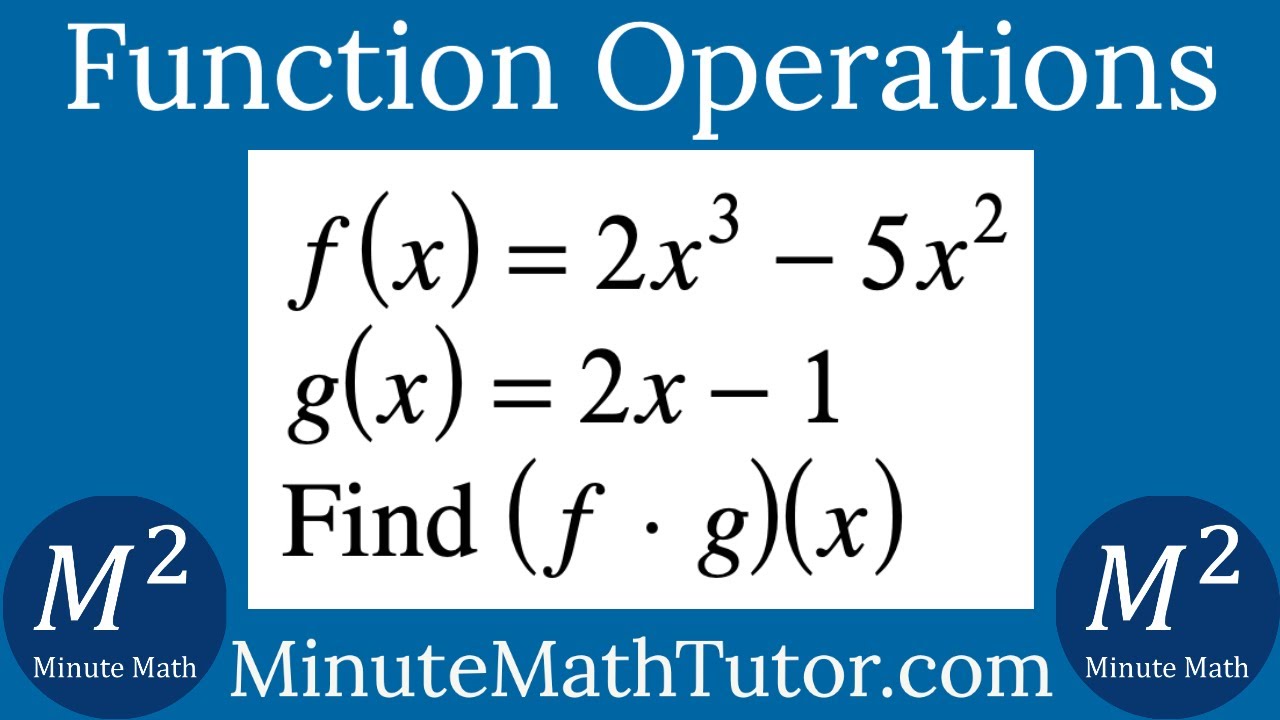



F X 2x 3 5x 2 G X 2x 1 Find F G X Youtube




F X X2 What Is G X Brainly Com



F X G X H X 1




F X X2 What Is G X Brainly Com




Precalculus Concepts Concavity Expii




F X X 2 What Is G X Brainly Com



F X X 2 What Is G X Apex



Solving Equations Graphically



What Is The Area Of The Region Enclosed By The Graphs Of F X X 2x 2 And G X 5x Quora
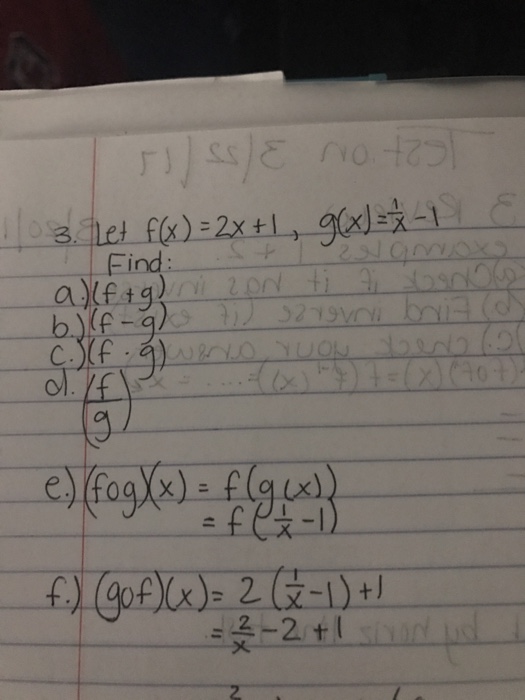



Let F X 2x 1 G X 1 X 1 Find A F G Chegg Com



Math Scene Equations Iii Lesson 3 Quadratic Equations




The Functions F X And G X Are Shown On The Graph F X X2 What Is G X A G X X2 2 B G X Brainly Com



Manipulating Graphs



Suppose F X X 2 What Is The Graph Of G X 1 3f X
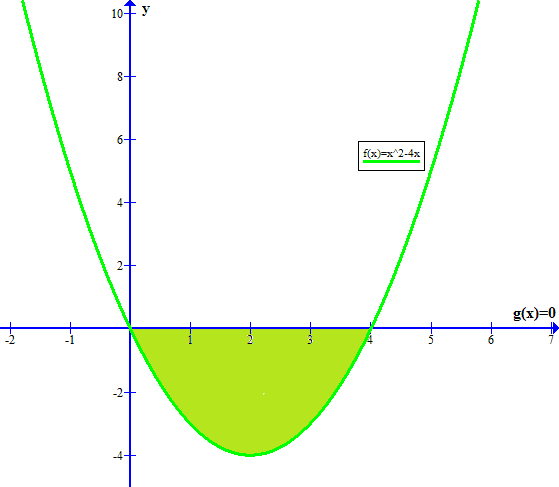



How Do You Find The Area Between F X X 2 4x G X 0 Socratic



Secure Media Collegeboard Org Digitalservices Pdf Ap Apcentral Ap15 Calculus Ab Q2 Pdf
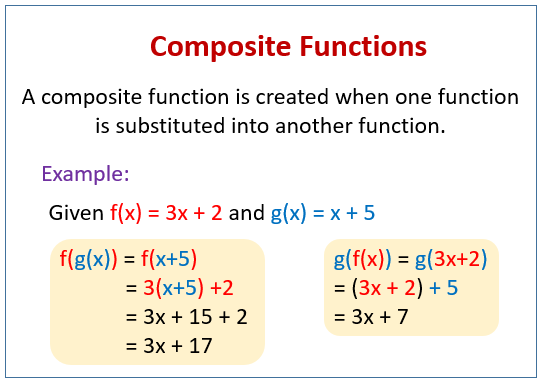



Composite Functions Video Lessons Examples And Solutions
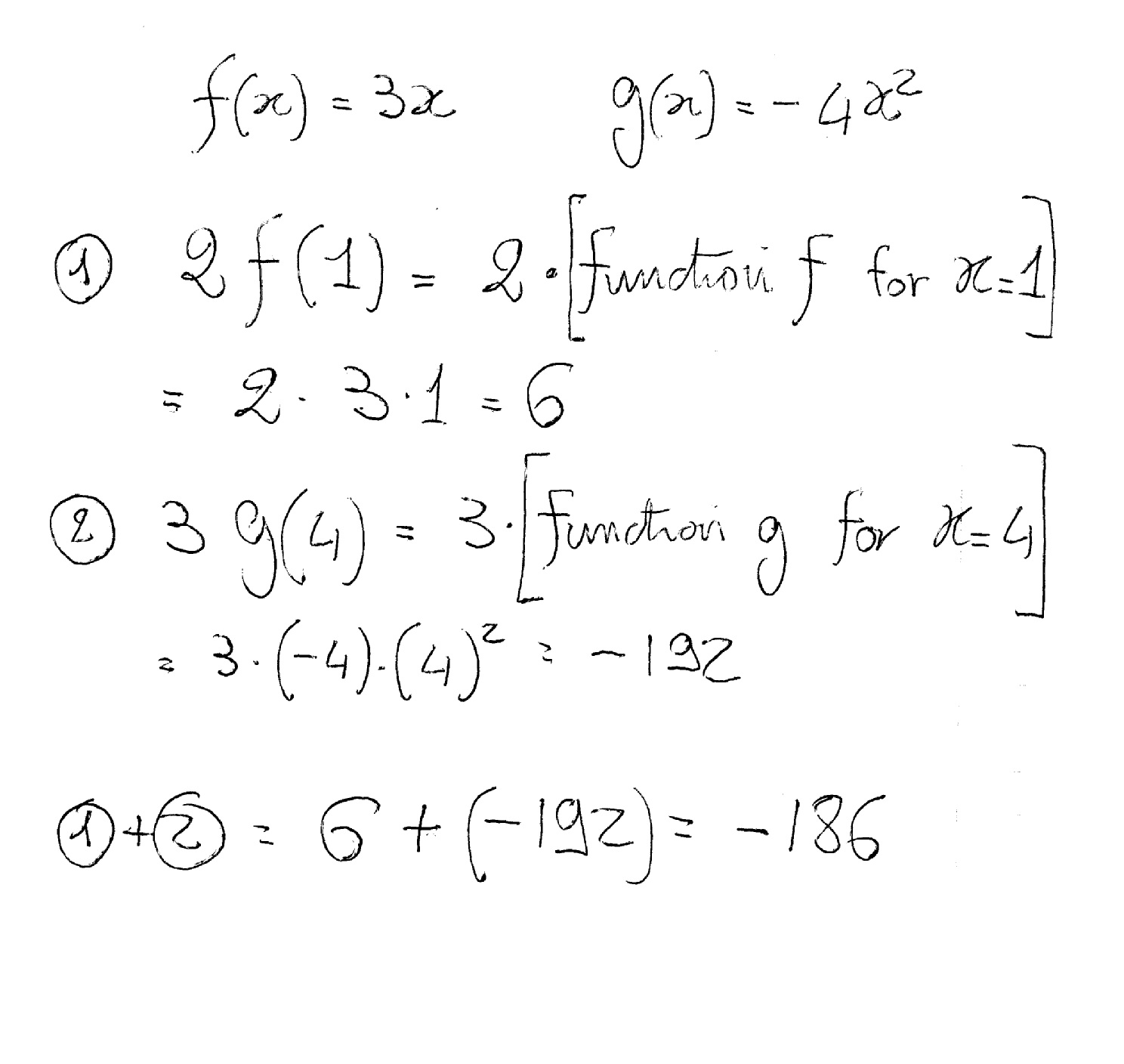



How Do Find The Value Of 2f 1 3g 4 If F X 3x And G X 4x 2 Socratic




If F X Sqrt X 2 1 G X X 1 X 2 1 And H X 2x 3 Then Find F Prime H Prime G Prime X



Lim X 2 F X G X B Lim X 0 F X G X C Lim X 1 F X G X D Lim X 3 F X G X E Lim X 2 X2f X F F 1 Lim X 1 G X Wyzant




Find 1 Gof And 2 Fog Where F X X 2 G X X 2 3x 1 Youtube




F X X 2 What Is G X Brainly Com




F X X 2 What Is G X Brainly Com



Given F X X2 2x And G X 6 X2 Find F G F G Fg And F G Youtube




F X X 2 What Is G X Brainly Com




Find Fog And Gof If F X Sinx G X X 2 Youtube
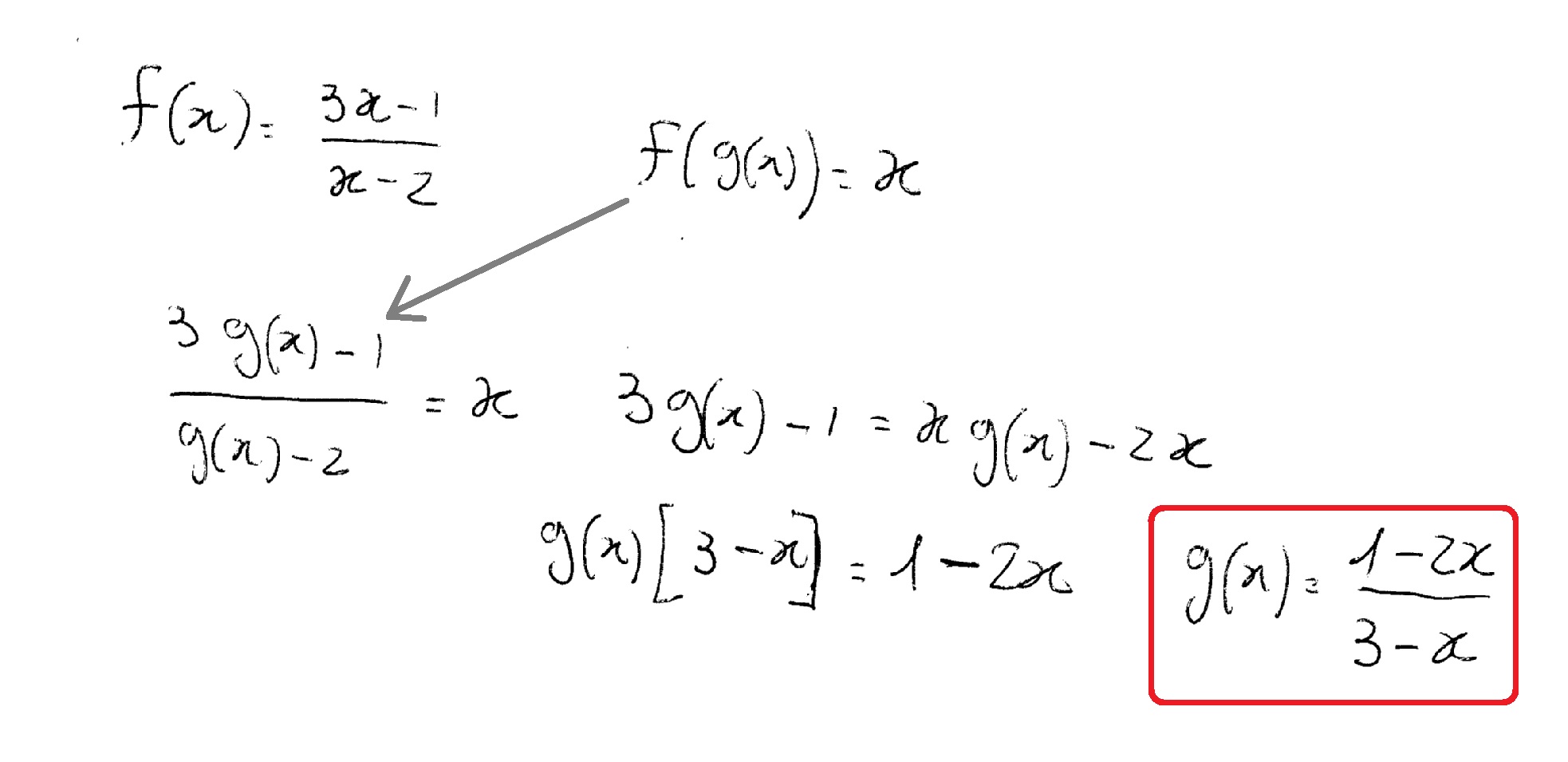



Let F X 3x 1 X 2 And F G X X How Do You Find G X Socratic




Quantitative Aptitude Algebra Functions Let F X X 2 And G X 2 X Handa Ka Funda Online Coaching For Cat And Banking Exams



Www Nhvweb Net Nhhs Math Psorg Files 11 08 Answers To 5 4 Function Operations Pdf




Warm Up Let F X Write The Equation For G X In Terms Of X 1 G X 3 F X 2 G X F 1 3x 3 G X F X 3 Ppt Download



Http Math Colorado Edu Nita Someexam2practicesol Pdf




Find A F G B F G C Fg And D F G And Chegg Com



Solution The Function F X X2 The Graph Of G X Is F X Translated To The Left 6 Units And Down 5 Units What Is The Function Rule For G X




F X X 2 What Is G X Brainly Com




Given That F X 2 X 4 And G X 3 X 5 Find Gf 3 With Noob Like Steps Please I Need A Really Clear Working To Fully Understand Thanks 3 Socratic



Solution If F X 2x 1 And G X X 2 Find 1 G G X 2 G F X 3 F G X 4 F F X




Example 16 Let F X X2 And G X 2x 1 Find F G Fg F G




F X X2 2x 1 G X 7x 5 F X X4 2x2 Chegg Com
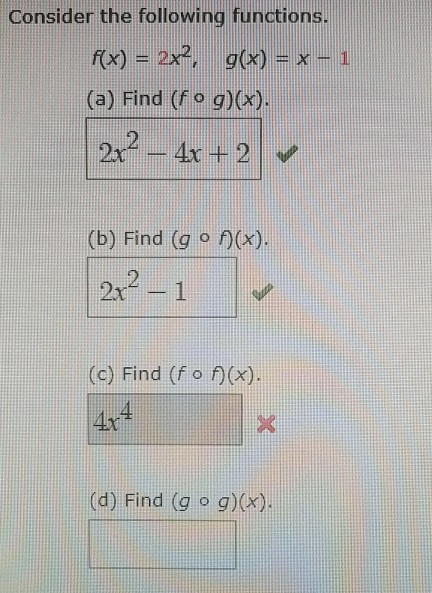



Consider The Following Functions X 2x2 A Chegg Com




F X X 2 What Is G X Brainly Com
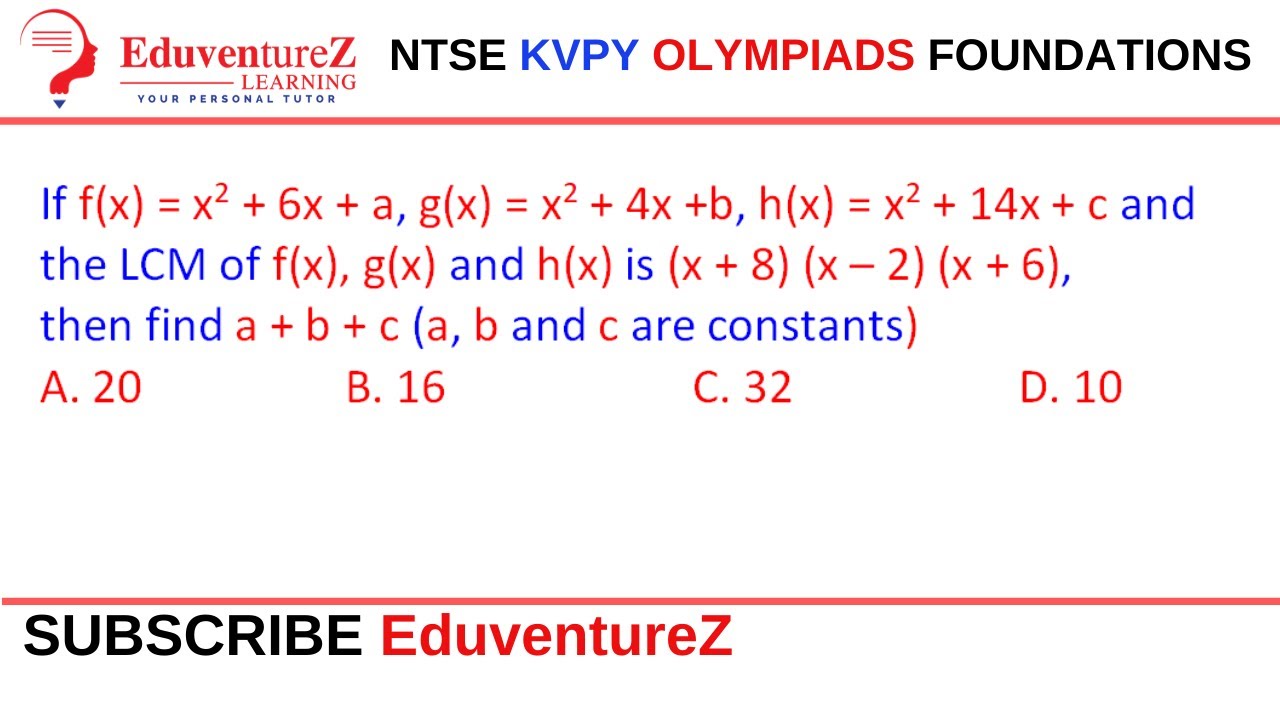



Q If F X X2 6x A G X X2 4x B H X X2 14x C And Youtube




F X X 2 What Is G X Brainly Com



Math Scene Equations Iii Lesson 3 Quadratic Equations




Answered The Functions F G And H Are Defined Bartleby




Consider The Following Functions F X X 2 G X Chegg Com




Consider The Following Functions F X X 2 G X Chegg Com



Http Www Midwayisd Org Cms Lib Tx Centricity Domain 164 Preap alg ii 6 3 Pdf



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿